Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback
Live Preview lets you preview the changes made to your entry before they're published to the live site. Content managers can preview draft content in real-time across multiple digital channels.
Note: The Live Preview feature currently works only for web-based applications. We will provide support for mobile-based applications in the future.
In this guide, we will learn how to set up the Live Preview feature for your stack using various frameworks with our SDKs.
We have a detailed step-by-step guide on how to set up Live Preview for your stack using three set up methods:
Let’s get started!
Server-side rendering (SSR) is the process where an application converts HTML files on a server instead of a browser into a rendered HTML client page. This guide explains in detail how to set up Live Preview for your SSR websites.
Steps for Execution
You must first set up your website. To do so, follow these steps given below:
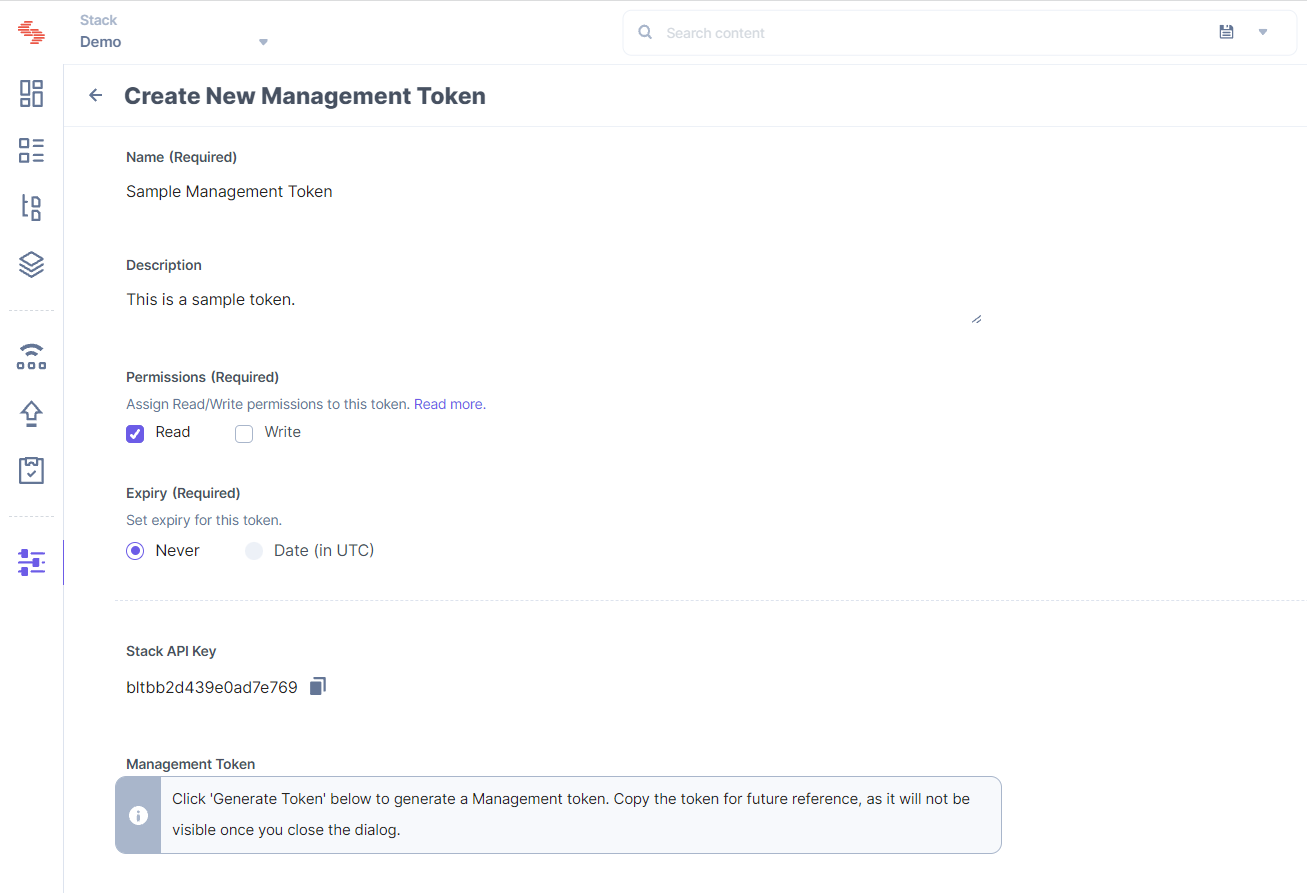
Contentstack.Stack() method of Contentstack's delivery SDK, e.g., here is a sample code for the JavaScript Delivery SDK:import Contentstack from 'contentstack'
const Stack = Contentstack.Stack({
...
// update your configs here
live_preview: {
management_token: management_token,
enable: true,
host: 'api.contentstack.io'
},
...
})Note: Set the host parameter to api.contentstack.io for the North America endpoint. If your website is hosted on the Europe data center, then pass eu-api.contentstack.com. Similarly, if it is hosted on the Azure NA, pass azure-na-api.contentstack.com
npm or import it using the script tag in your HTML page code.script tag of the HTML file, add the following code:<script src="https://unpkg.com/@contentstack/live-preview-utils@^1.2/dist/index.js"></script>
init() method.<script>
ContentstackLivePreview.init();
</script>npm install @contentstack/live-preview-utils
init() method. This method helps set up event listeners that keep a tab of any changes made to the previewed entry's content.import ContentstackLivePreview from "@contentstack/live-preview-utils"; ContentstackLivePreview.init();
Note: You need to define your SDK initialization code within a separate JavaScript file to prevent configuration resetting errors in your Live Preview setup caused by rerendering.
Stack class using the livePreviewQuery() method.app.use((req, response, next) => {
// this will get live_preview hash and ContentType to the request
Stack.livePreviewQuery(req.query);
next();
});With these steps, we have the user website ready. Let's move ahead and host this website.
To host a website, you can simply use ngrok or any other website hosting service.
Note: Make sure your website is HTTPS enabled.
To enable Live Preview through the stack settings in Contentstack, follow the steps given below:
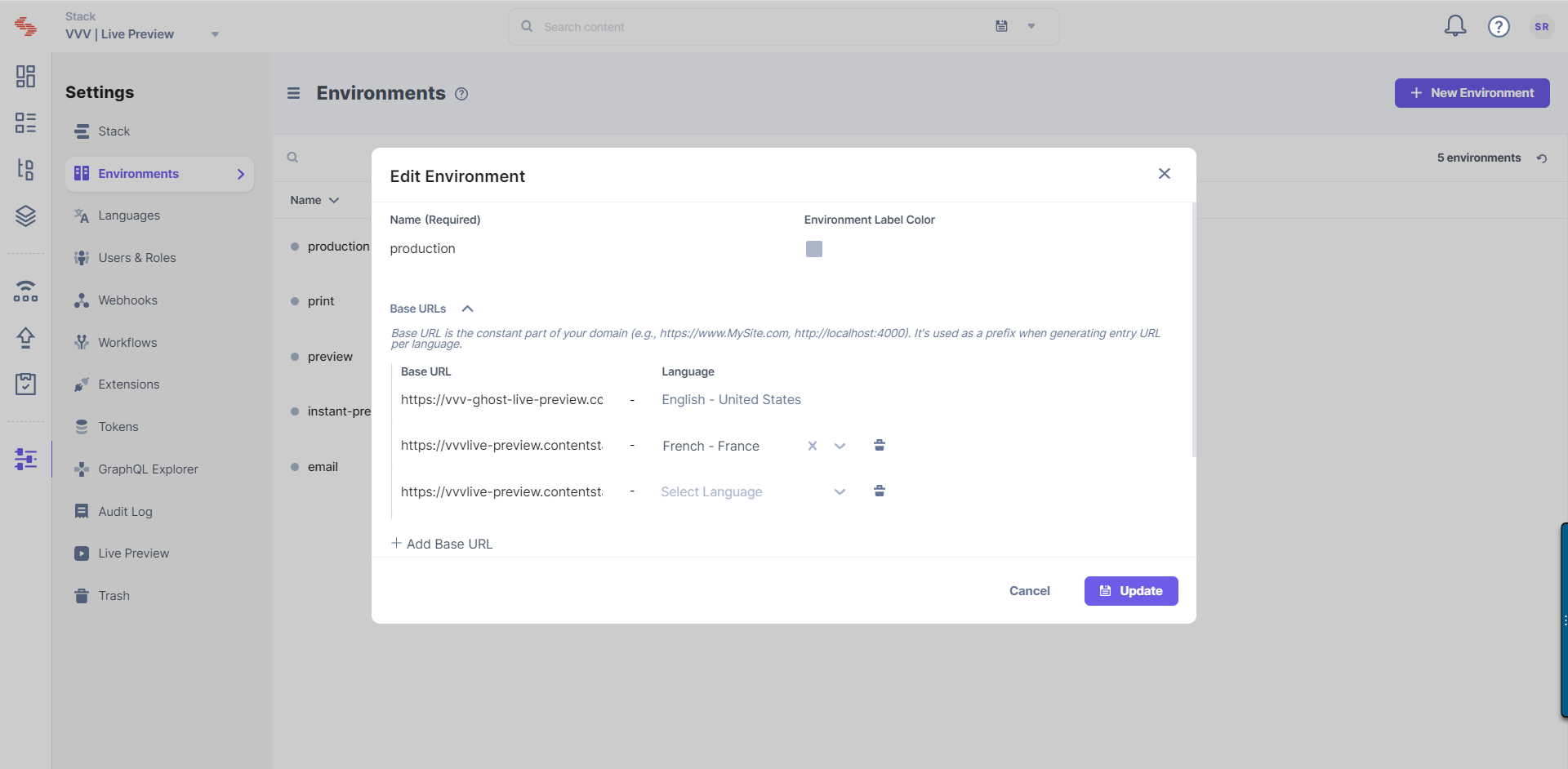
Tip: You can also update the preview URL and environment from the preview settings available on the entry page.
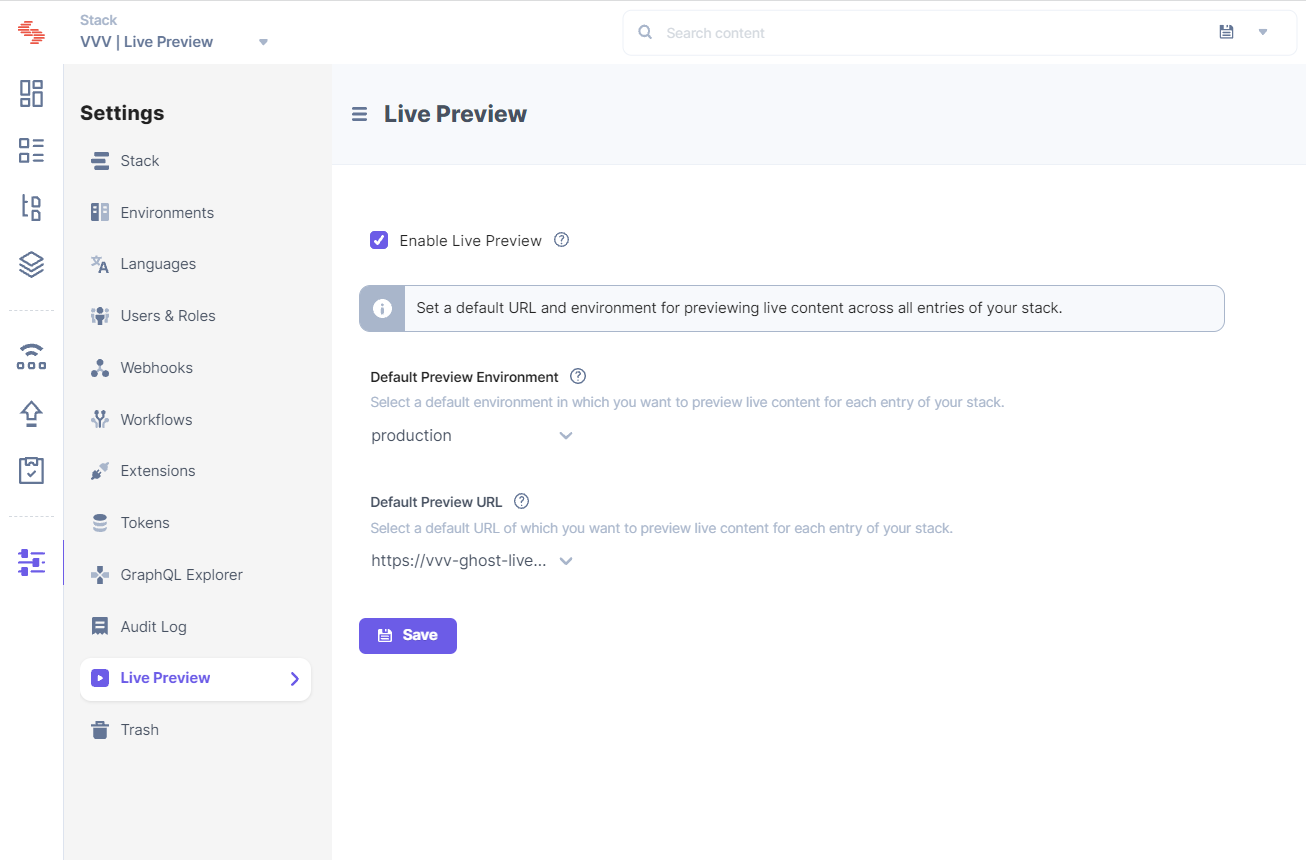
Tip: Once you have set up Live Preview for your stack, you can refer to the Live Editing for Entries section to learn how to set up real-time content editing and preview for stack entries.
You will now be able to see the Live Preview icon within all the entries of your stack and the feature will preview data from the hosted website.
Client-side rendering (CSR) is where developers render their content directly to a browser using JavaScript. This guide explains in detail how to set up Live Preview for your CSR websites.
Steps for Execution

Contentstack.Stack() method of Contentstack's delivery SDK, e.g., here is a sample code for the JavaScript Delivery SDK:import Contentstack from 'contentstack'
const Stack = Contentstack.Stack({
...
// update your configs here
live_preview: {
management_token: management_token,
enable: true,
host: 'api.contentstack.io'
},
...
})Note: Set the host parameter to api.contentstack.io for the North America endpoint. If your website is hosted on the Europe data center, then pass eu-api.contentstack.com. Similarly, for the Azure NA region, pass azure-na-api.contentstack.com
npm or import it using the script tag in your HTML page code.script tag of the HTML file, add the following code:<script src="https://unpkg.com/@contentstack/live-preview-utils@^1.2/dist/index.js"></script>
init() method.<script>
ContentstackLivePreview.init();
</script>npm install @contentstack/live-preview-utils
init() method. This method helps set up event listeners that keep a tab of any changes made to the previewed entry's content.Stack object against the stackSDK parameter.import ContentstackLivePreview from "@contentstack/live-preview-utils";
ContentstackLivePreview.init({
stackSdk: Stack,
});Note: You need to define your SDK initialization code within a separate JavaScript file to prevent configuration resetting errors in your Live Preview setup caused by rerendering.
onEntryChange() method will be executed. You can define any coding logic that helps fetch data inside this method.updateData() function responsible for fetching the data and setting it to React state.useEffect function, we pass the updateData function against the onEntryChange() method. This onEntryChange() method runs the updateData() function every time you update entry content.// utils.js
...
export const onEntryChange = ContentstackLivePreview.onEntryChange;
...
// Footer.js
import React from "react";
import { onEntryChange } from "./utils.js";
const Footer = () => {
const [data, setData] = React.useState({});
const updateData = () => {
const fetchedData = SomeCallToGetData();
setData(fetchedData);
};
React.useEffect(() => {
onEntryChange(updateData);
}, []);
return <div>{data.company_name}</div>;
};To host a website, you can simply use ngrok or any other website hosting service.
To enable Live Preview through the stack settings in Contentstack, follow the steps given below:

Tip: You can also update the preview URL and environment from the preview settings available on the entry page.

Tip: Once you have set up Live Preview for your stack, you can refer to the Live Editing for Entries section to learn how to set up real-time content editing and preview for stack entries.
You will now be able to see the Live Preview icon within all the entries of your stack and the feature will preview data from the hosted website.
Gatsby is an open-source framework that combines functionality from React, GraphQL and Webpack into a single tool for building static websites and apps. This guide explains in detail how to set up Live Preview for your Gatsby-powered websites.
Steps for Execution

Contentstack.Stack() method of Contentstack's delivery SDK, e.g., here is a sample code for the JavaScript Delivery SDK:import Contentstack from 'contentstack'
const Stack = Contentstack.Stack({
...
// update your configs here
live_preview: {
management_token: management_token,
enable: true,
host: 'api.contentstack.io'
},
...
})Note: Set the host parameter to api.contentstack.io for the North America endpoint. If your website is hosted on the Europe data center, then pass eu-api.contentstack.com. Similarly, for Azure NA data center, pass azure-na-api.contentstack.com.
npm or import it using the script tag in your HTML page code.script tag of the HTML file, add the following code:<script src="https://unpkg.com/@contentstack/live-preview-utils/dist/index.js"></script>
init() method.<script>
ContentstackLivePreview.init();
</script>npm install @contentstack/live-preview-utils
init() method. This method helps set up event listeners that keep a tab of any changes made to the previewed entry's content.Stack object against the stackSDK parameter.import ContentstackLivePreview from "@contentstack/live-preview-utils";
ContentstackLivePreview.init({
stackSdk: Stack,
});Note: You need to define your SDK initialization code within a separate JavaScript file to prevent configuration resetting errors in your Live Preview setup caused by rerendering.
onEntryChange() method will be executed. Hence, you can define any coding logic that helps fetch data inside this method.updateData() function responsible for fetching the data and setting it to React state.useEffect function, we pass the updateData function against the onEntryChange() method. This onEntryChange method runs the updateData() function every time you update entry content.// utils.js
...
export const onEntryChange = ContentstackLivePreview.onEntryChange;
...
// Footer.js
import React from "react";
import { onEntryChange } from "./utils.js";
const Footer = () => {
const [data, setData] = React.useState({});
const updateData = () => {
const fetchedData = SomeCallToGetData();
setData(fetchedData);
};
React.useEffect(() => {
onEntryChange(updateData);
}, []);
return <div>{data.company_name}</div>;
};Finally, Gatsby primarily gets its data from contentstack-source-plugin. But, Live Preview currently works only on JavaScript Content Delivery SDK. Hence, for Gatsby, we fetch the data from the contentstack SDK, store it to React state, and rerender the page using the onEntryChange() method.
The data format remains different for the Gatsby source plugin. It requires a prefix and the entry names are in Camel case. Hence, we use getGatsbyDataFormat() to convert the entry's name.
It takes the Contentstack Stack object as the first parameter and the prefix as the second. The prefix is set inside the gatsby-config.js file. The default value of the prefix is contentstack.
// for example:
const query = Stack.ContentType("your-contentype").Entry("entry-uid");
const formattedData = ContentstackLivePreview.getGatsbyDataFormat(
query,
"contentstack"
);
setData(formattedData);Together, the code will look as follows:
// utils.js
...
export const onEntryChange = ContentstackLivePreview.onEntryChange;
...
// Footer.js
import React from "react";
import { onEntryChange } from "./utils.js";
const Footer = () => {
const [data, setData] = React.useState({});
const updateData = () => {
const query = Stack.ContentType("your-contentype").Entry("entry-uid");
const fetchedData = ContentstackLivePreview.getGatsbyDataFormat(
query,
"contentstack"
);
setData(fetchedData);
};
React.useEffect(() => {
onEntryChange(updateData);
}, []);
return <div>{data.company_name}</div>;
};To host a website, you can simply use ngrok or any other website hosting service.
To enable Live Preview through the stack settings in Contentstack, follow the steps given below:

Tip: You can also update the preview URL and environment from the preview settings available on the entry page.

Tip: Once you have set up Live Preview for your stack, you can refer to the Live Editing for Entries section to learn how to set up real-time content editing and preview for stack entries.
You will now be able to see the Live Preview icon within all the entries of your stack and the feature will preview data from the hosted website.
Live edit tags allow you to navigate to the field that contains the website content being previewed within the Live Preview pane. When you click on the "Edit" button beside a content block in the preview pane, you will be redirected to the corresponding field within the entry. If the field holds reference to another entry, you will be redirected to the referenced entry's editor page.
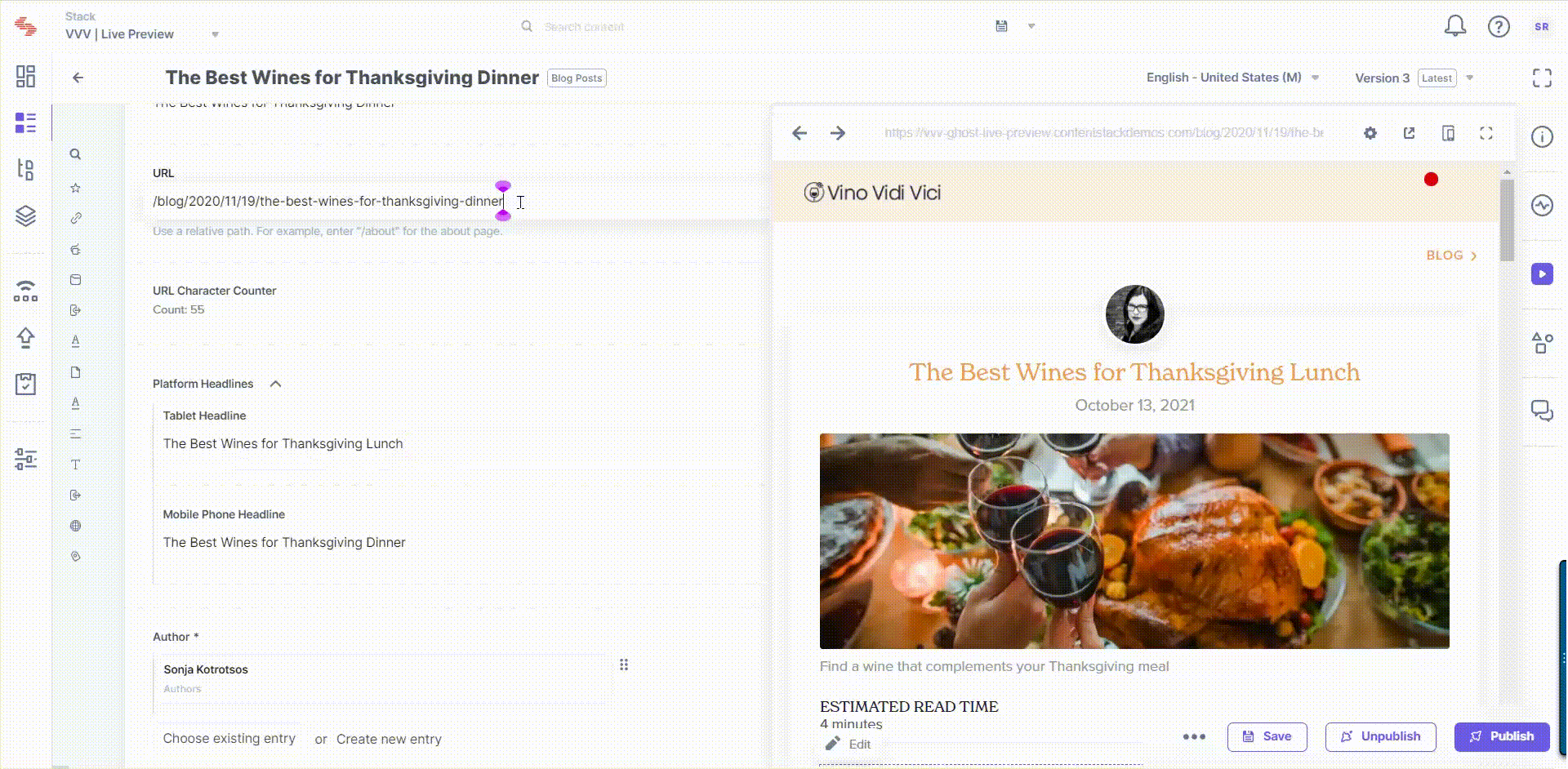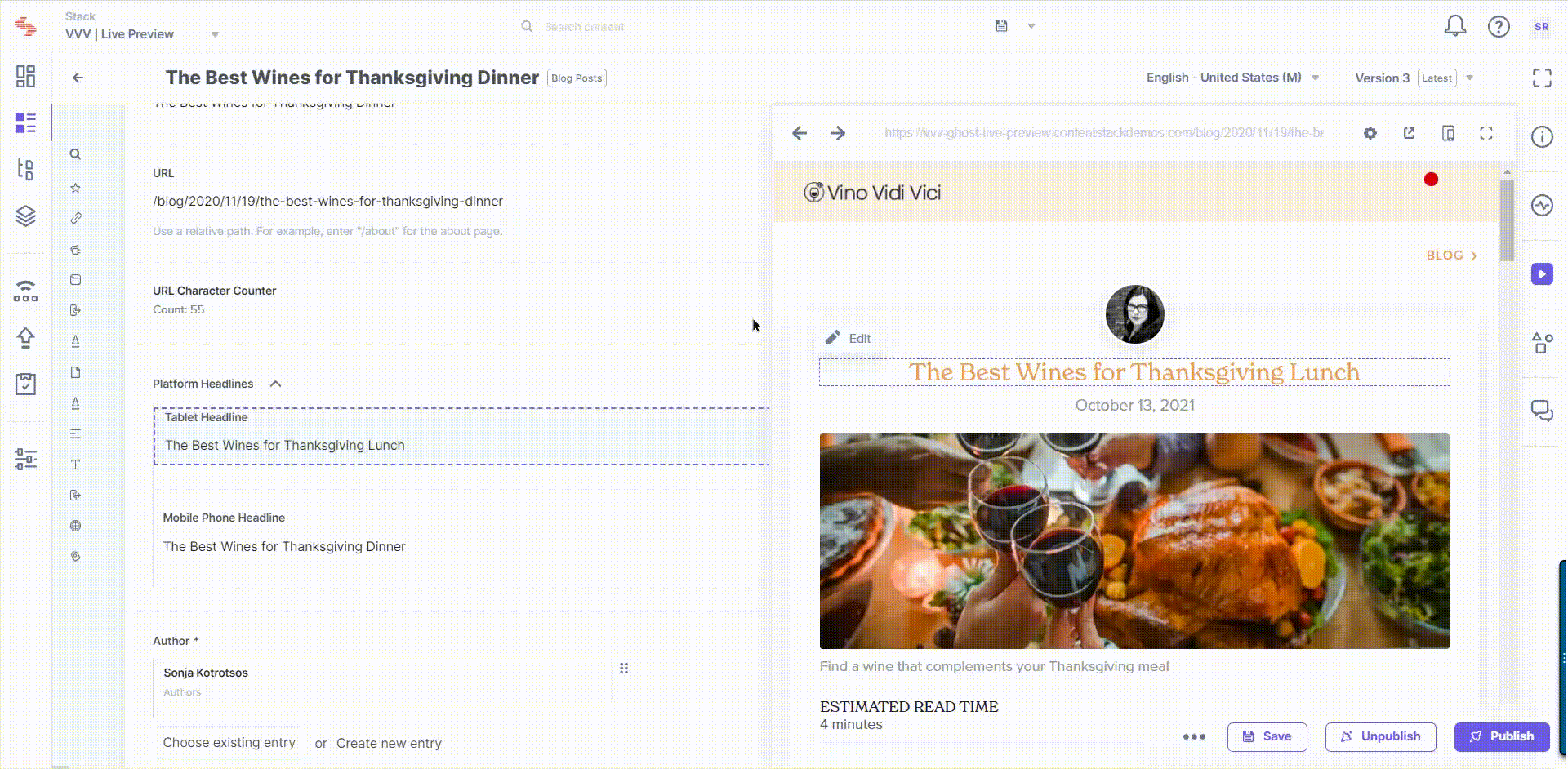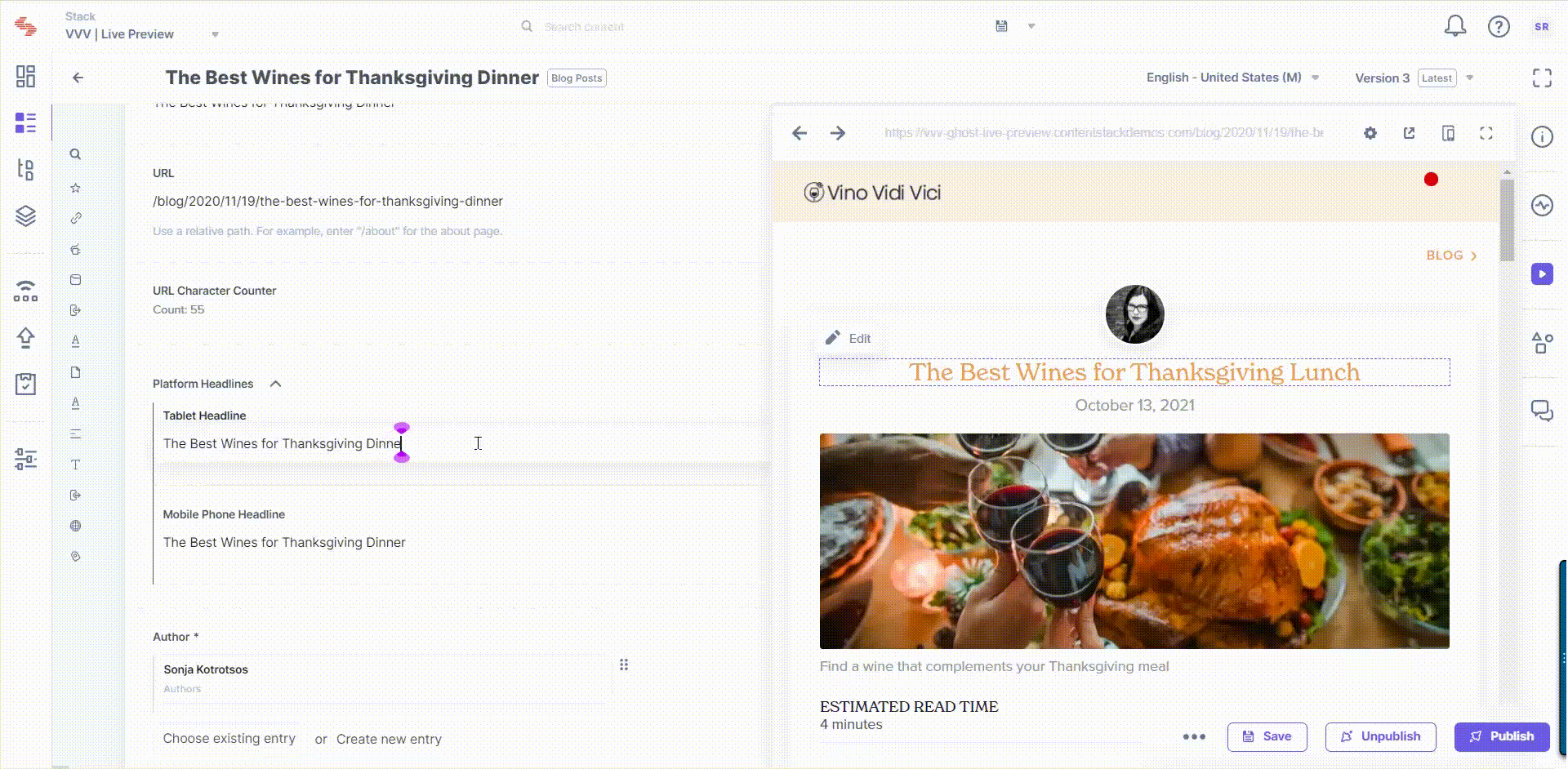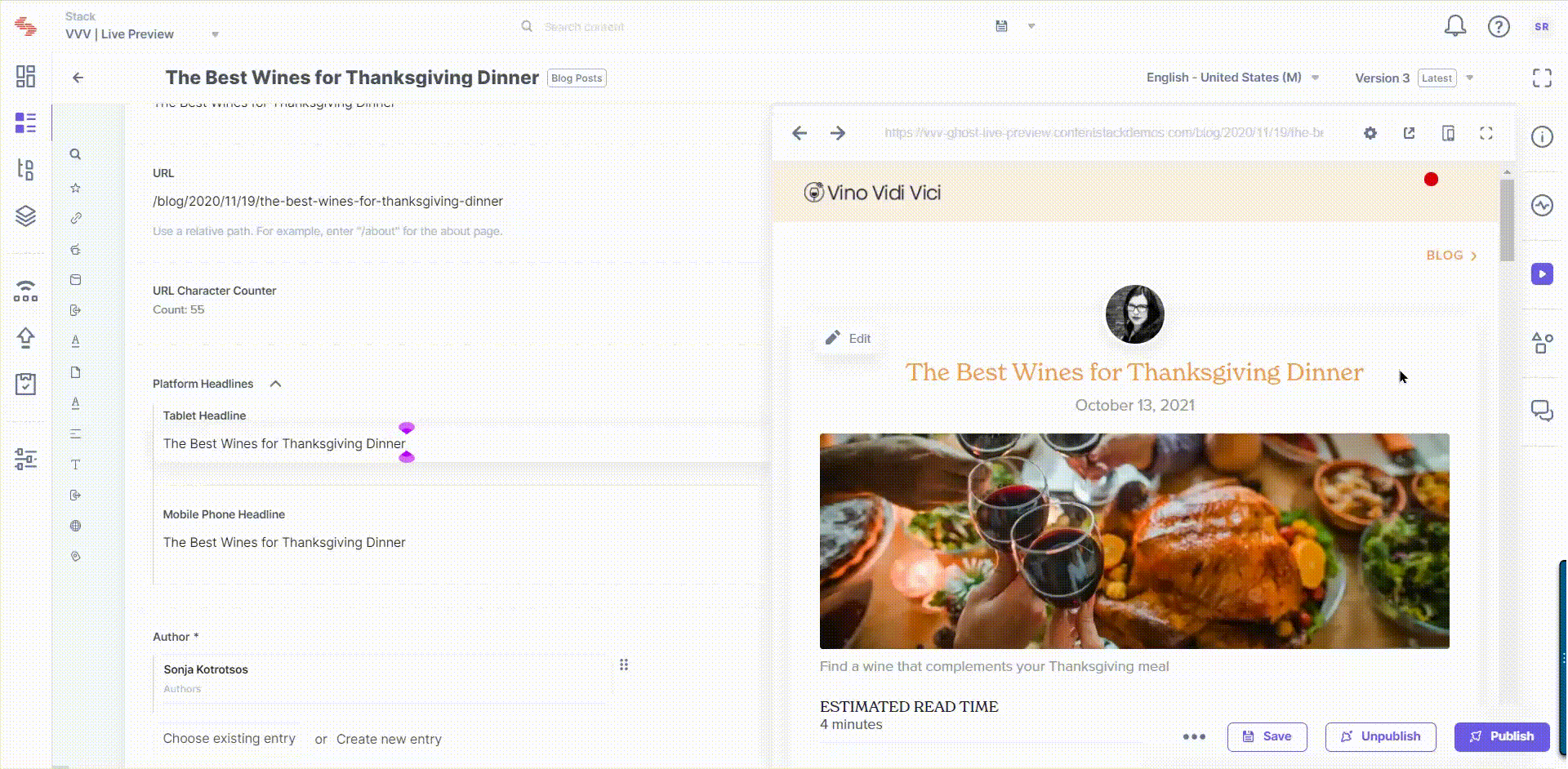
Edit tags contain the location where the corresponding field lies within the entry. The Live Preview Utils SDK searches for the elements which contain the edit tags referred to as data-cslp.
The structure of the edit tag (field location in the entry) you can pass against the data-cslp attribute is as follows:
{content_type_uid}.{entry_uid}.{locale}.{field_uid}Here's a sample field path:
home.blt80654132ff521260.en-us.modular_blocks.block_1.media_group_uid.image_uid
Note: If the field is nested within another complex field, such as Modular Blocks, provide the field path as follows: {modular_block_field_UID}.{block_UID}.{field_UID}.
For a website built using Contentstack's JavaScript Delivery SDK, we use the addEditableTags() method to automatically generate the edit tag for you. The following section explains how you can set up live edit tags using addEditableTags().
Stack.ContentType() method.Stack.ContentType() method:let entry = await Stack.ContentType("content_type_uid").Query()
.where("url", URL)
.find();addEditableTags() method from the Contentstack SDK:const Contentstack = require("contentstack");
Contentstack.Utils.addEditableTags()Note: The addEditableTags() method is also available in the Contentstack JavaScript Utils SDK package.
addEditableTags() function to add edit tags to the previewed entry content:addEditableTags(entry, content_type_uid, tagsAsObject, locale)
entry is the actual entry you get from the SDK, content_type_uid is the unique ID of the current entry’s content type, and tagsAsObject determines the format in which the edit tag would be added.Note: The addEditableTags() method does not return any value. It only modifies the entry passed as the first argument to the method.
tagsAsObject is set to false, and it appends data-cslp in the form of a string as follows:'data-cslp=path.to.field'
Note: This option is provided for React-based apps as we cannot directly add any attributes in string format. Instead, we need to destructure an object.
tagsAsObject is set to true, the data-cslp attribute is returned in object format as follows:{ 'data-cslp': 'path.to.field'}addEditableTags() method:let entry = await Stack.ContentType("content_type_uid").Query()
.where("url", URL)
.find();
addEditableTags(entry[0][0], "content_type_uid", false)
addEditableTags() method, a new key-value pair is returned at every level in the existing entry schema. This pair is known as the edit tag and is denoted by a dollar sign ($).addEditableTags() method:{
"name": "John Doe",
"description": {
"occupation": [{
"name": "Plumber",
"since": 1920
}],
"height": "5ft"
}
}
addEditableTags() method is executed, the entry passed against the first parameter is updated as follows:{
"name": "John Doe",
"$": {
"name": "profile.blt8tvsk328dbw258.en-us.name"
},
"description": {
"$": {
"occupation": "profile.blt8tvsk328dbw258.en-us.description.occupation",
"height": "profile.blt8tvsk328dbw258.en-us.description.height"
},
"occupation": [{
"$": {
"name": "profile.blt8tvsk328dbw258.en-us.description.occupation.name",
"since": "profile.blt8tvsk328dbw258.en-us.description.occupation.since"
},
"name": "Plumber",
"since": 1920
}],
"height": "5ft"
}
}
ContentstackLivePreview.init({
...
stackDetails: {
apiKey: "your api key",
},
clientUrlParams: {
protocol: "https",
host: "app.contentstack.com",
port: 443,
},
})ClientUrlParams key is optional and is set for the North America region. For Europe region, you can use the following config for clientUrlParams:{
host: "eu-app.contentstack.com",
}{
host: "azure-na-app.contentstack.com",
}data.description.height, then the corresponding edit tag will be data.description.$.height.<header class="text-center">
<div class="author">
<img {{ data.author.profile_image.$.url }} src="{{ data.author.profile_image.url }}" alt="{{ data.author.title }}" />
</div>
<h1 {{ data.author.$.title }}>{{ data.author.title }}</h1>
<h2 class="author-job" {{ data.author.$.job_title }}>{{ data.author.job_title }}</h2>
<p class="author-bio" {{ data.author.$.biography }}>{{ data.author.biography }}</p>
<div class="author-social">
<a href="mailto:{{ data.author.social.email }}"><ion-icon name="mail-outline"></ion-icon></a>
<a href="https://www.twitter.com/{{ data.author.social.twitter }}"><ion-icon name="logo-twitter"></ion-icon></a>
<a href="https://www.instagram.com/{{ data.author.social.instagram }}"><ion-icon name="logo-instagram"></ion-icon></a>
</div>
</header>tagsAsObject parameter to true. When set to true, this parameter returns the edit tag in object format. You need to destructure the object while passing it within the JSX element.<h1 {...data.$.name}>{data.name}</h1>
<p {...data.description.$.height}>{data.description.height}</p>Note: This setup only works for generic websites that use basic JavaScript frontend code. For websites working on other programming languages, you need to provide the entire path to the specific field.
@contentstack/live-preview-utils/dist/main.css file. You can import these styles in your main index.js file using npm as follows:import "@contentstack/live-preview-utils/dist/main.css";
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://unpkg.com/@contentstack/live-preview-utils/dist/main.css">
Once you have configured the settings, you will be able to see the Edit icon whenever you hover over a content block in your preview pane.
![]()
Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback