Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback
Releases in Contentstack help you to create a set of entries or assets you want to deploy (for publishing or unpublishing). This is, however, a manual task where you need to create a release and add items to it. If you add items to a release frequently this manual process can be cumbersome.
In this guide, we will look at the steps required to create an automated system for scheduling repeatable releases using AWS Lambda and Contentstack's Content Management APIs.
Once the system creates a release automatically, you can add items (entries and assets) to it, and they will be deployed automatically at the scheduled time. This is a continuous process where the release gets created every day, and if there are items added to it, they get deployed.
In this example, we will use two Lambda Functions: one for creating a release and another one for deploying the release. The “create release” lambda function will create a new release for every new day. For example, a release will be scheduled every midnight after 12:00 AM, a new day, and create a release for this specific day using the Releases API.
Note: You can change the date as per your convenience, but ensure that it is after 12:00 AM or a new date 00:01 (24 hr format).
In the following image, you can see that Thu May 14 2020 is the release name and created by using the Create Release Lambda function every new day for entries and assets required to be deployed on that day, that is, “Thu May 14 2020.
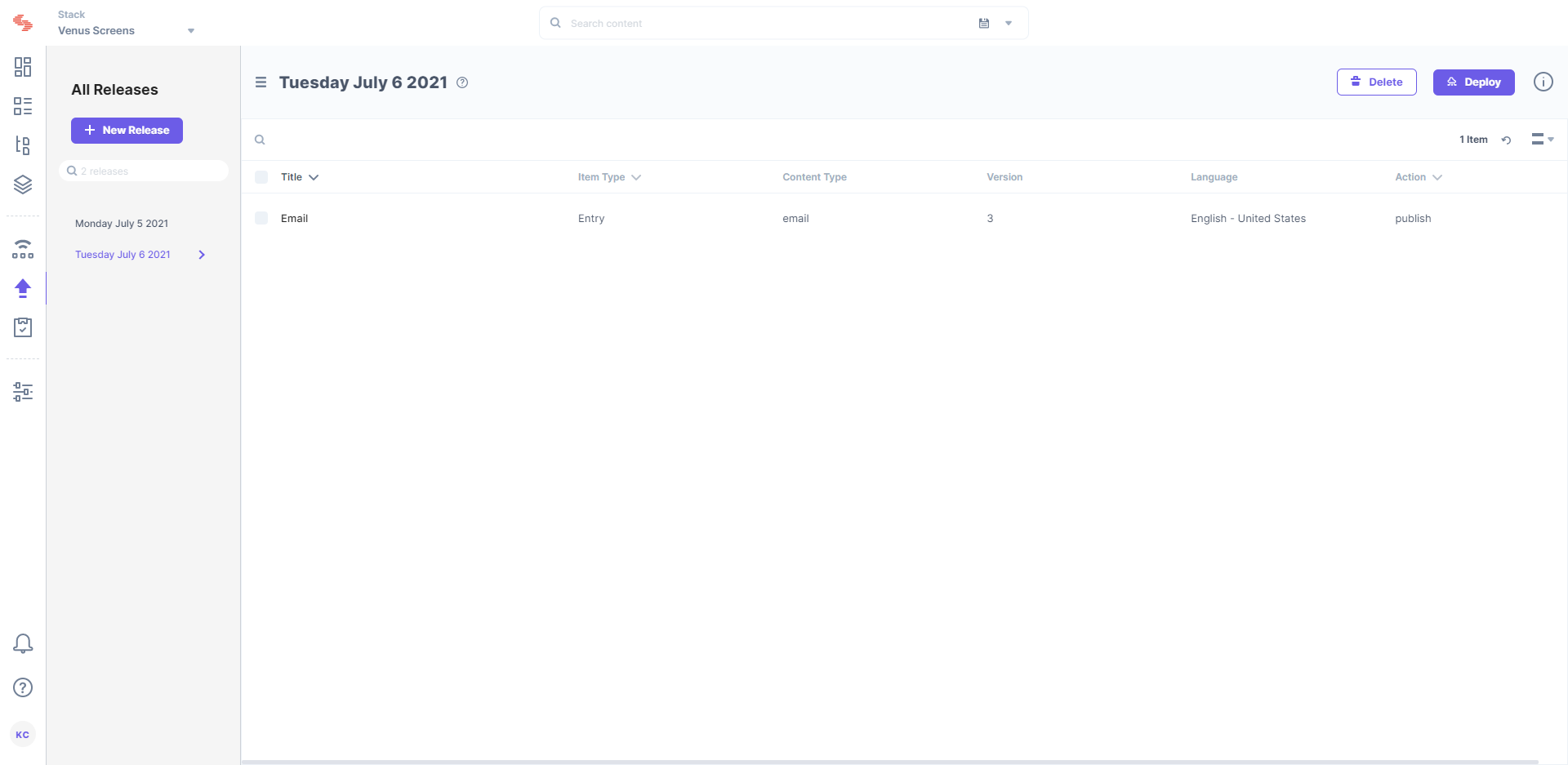
The Deploy Release Lambda Function deploys the release created on that specific date. For example, if the release is scheduled for “Thu May 14 2020,” the Deploy Release lambda will look for a release created for that day.
If the lambda function detects any release for the scheduled day, it then fetches that release’s UID and checks for any entries/assets within the release. And if there are any entries or assets within that release, it deploys the release. If there are no entries or assets for deployment in the release, it does nothing as there is nothing to deploy.
The next day, the Create Release lambda function will be triggered again to create another release. And this continues making it repeatable. If the release with entries and assets is deployed, it locks the release (as shown in the above screenshot), and you cannot access it for adding new entries or assets (it will be disabled).
Note: These lambda functions can be “enabled” or “disabled” to stop lambda from creating and deploying releases.
Let's now move ahead with the steps and create the required system.
For the Lambda function to create and deploy release(s), you’ll need a management token having read and write access. To generate one, perform the steps specified in the Generate Management Token guide.
Download the code for the Create Release and Deploy Release lambda functions from our Github page.
Unzip the downloaded code and open your terminal (command prompt). Point it to the createRelease code folder, and run the following command to install the required dependencies:
npm install
Likewise, install dependencies for the deployRelease code folder as well.
Finally, zip the createRelease and deployRelease code folders as you’ll need to upload them to AWS Lambda.
Perform the following steps to set up a lambda function that will help us create the releases automatically:
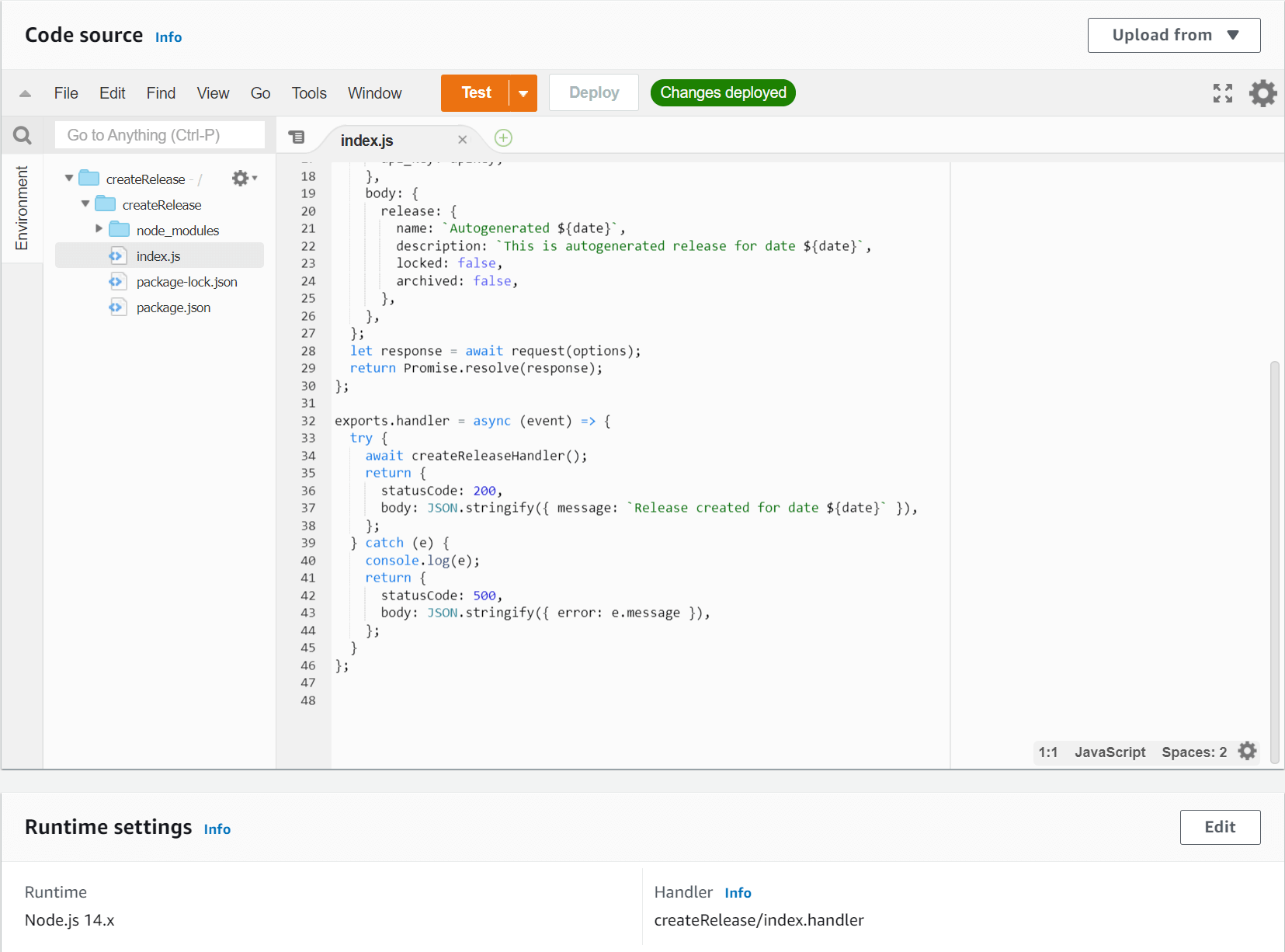
To add environment variables, go to the Configuration tab, click on Environment variables, then click Edit button, and then add the following environment variables:
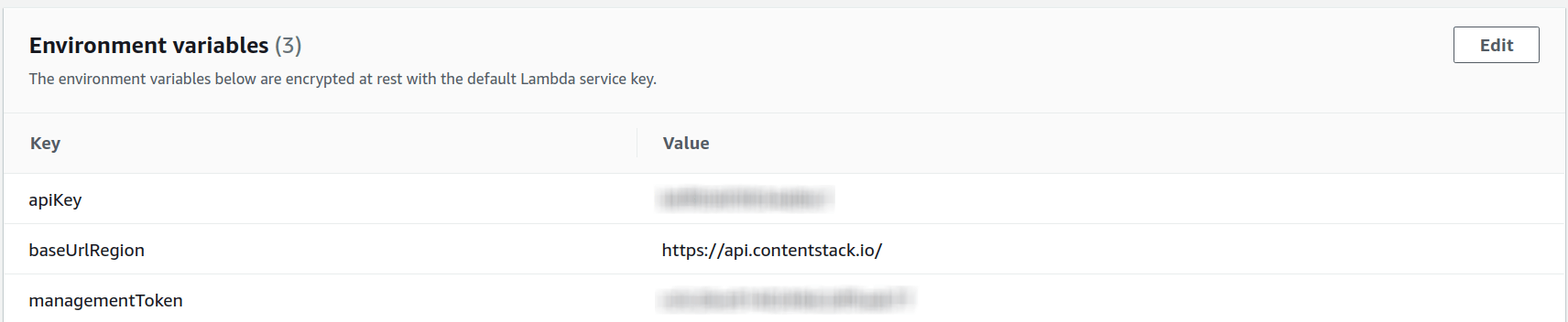
Additional Resources: Refer to Cron-Generator and AWS-guide-on-using-cron for more information. Also, refer to the AWS guide on How-to-schedule-lambda-using-cloudwatch-events.
For the Create Release Lambda Function, the scheduled cron expression that we just set will trigger on cron(00 01 * * ? *), that is, at 1:00 AM (which will be on a new day). You can adjust the scheduled cron expression but make sure it is on a new date, that is, after 12:00 AM.Note: You can use cron or rate expression to create self-trigger rules on an automated schedule in CloudWatch Events. All your created scheduled events use the UTC time zone with the minimum precision of 1 minute for the schedule.
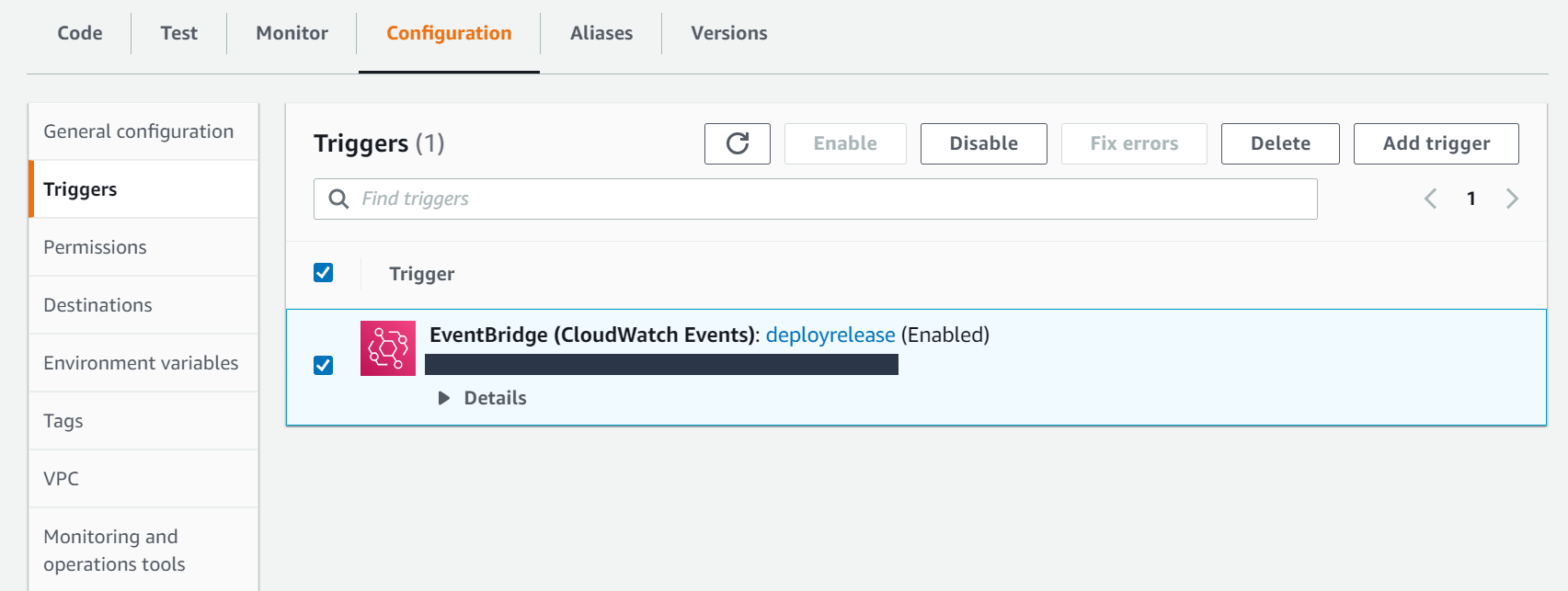
After you have set up the trigger, this is how it will look in the Lambda dashboard: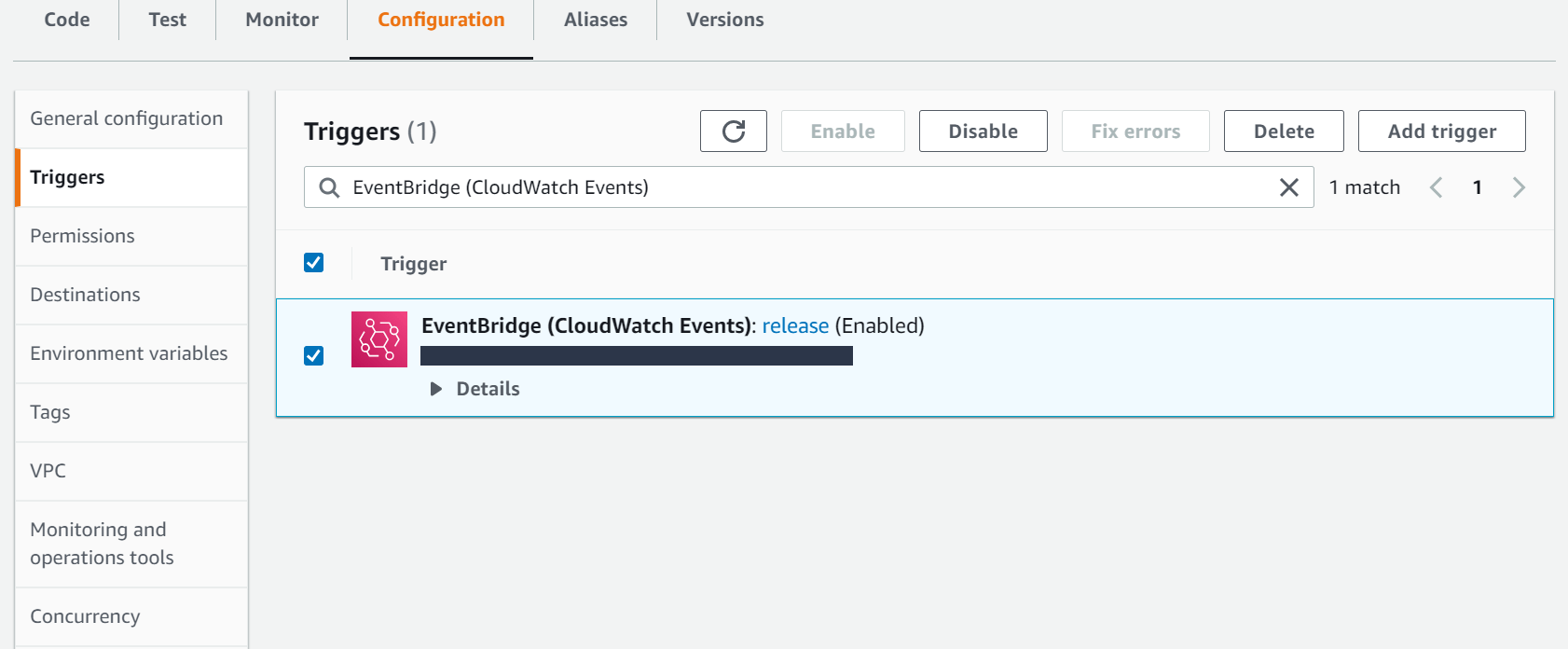
Note: You can disable or enable events rules using the options shown in the above screenshot.
Perform the following steps to set up a lambda function to deploy release automatically:
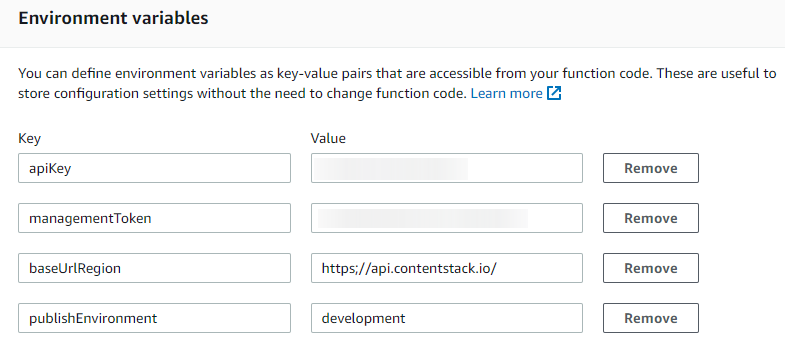
Note: If you plan to deploy your release on multiple environments, you can click on the Add environment variable button and add more environments. If you have added more environment for deployment make sure to add the name of those environments in the deployRelease code as shown:
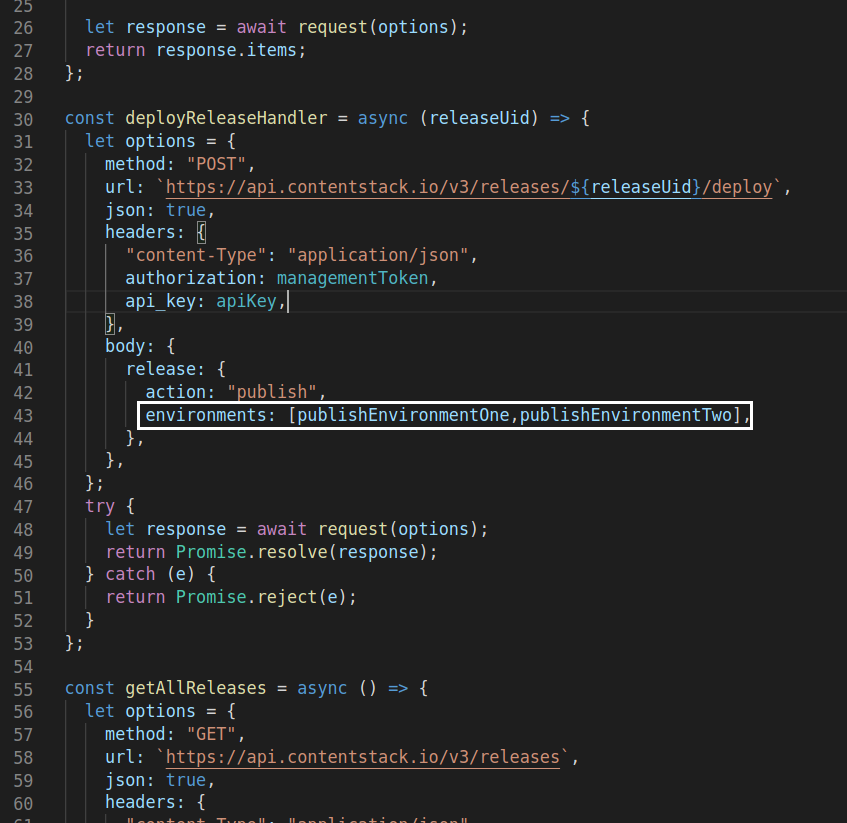
Note: You can disable or enable events rules using the options as shown in the above screenshot.
With these steps, we have the set up ready. On the scheduled time and date, the lambda function to create release will be invoked, thus creating a release. Likewise, the lambda function to deploy a release function will be invoked at the scheduled time, deploying the release if it contains any entries or assets.
Once the release is created, this is how appears
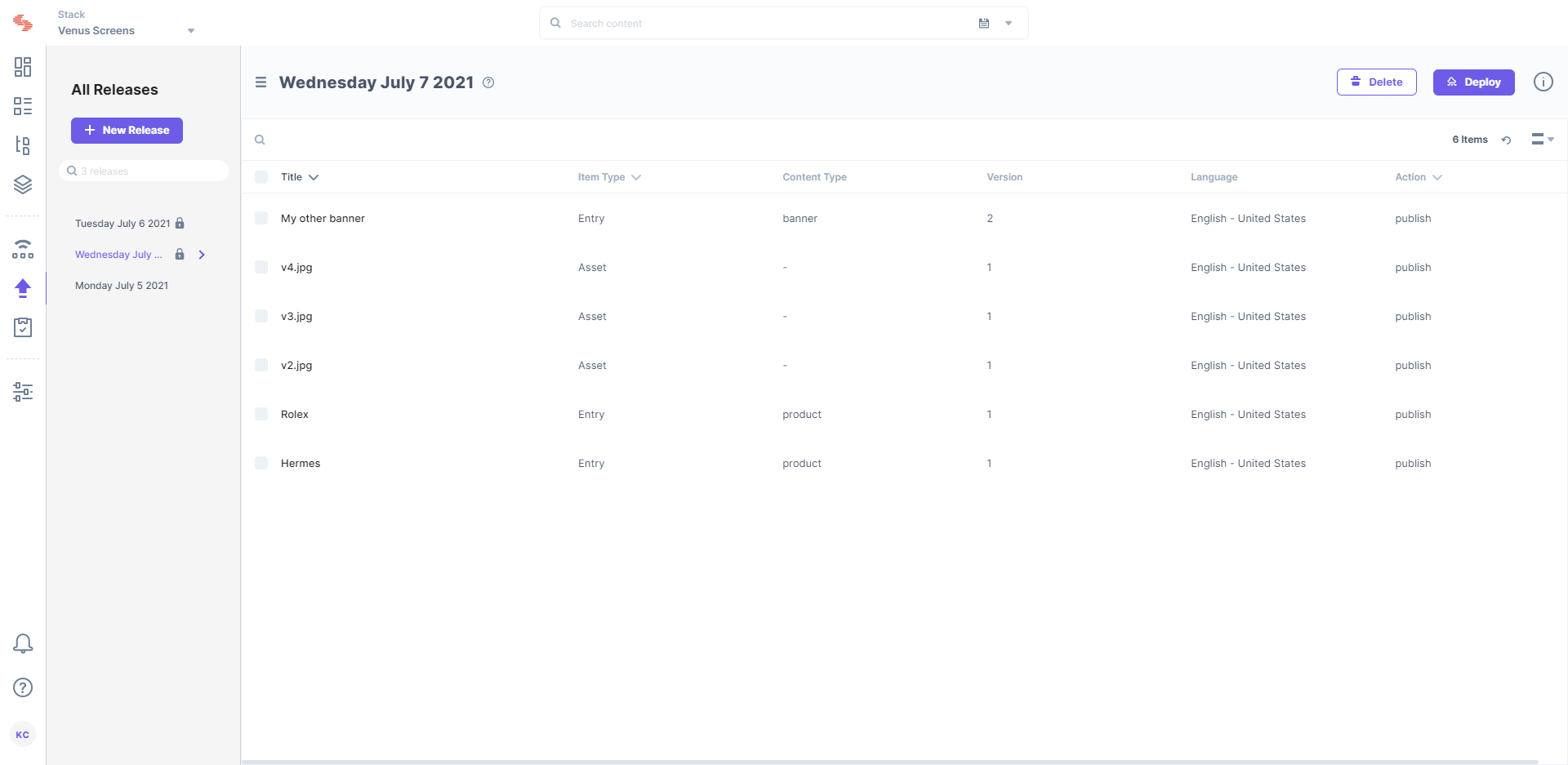
We have created various other guides that cover the use of AWS Lambda functions. You may refer to our Webhook Integrations page for more details.
Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback