Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback
Constructor.io is a cloud-based product discovery solution designed for enterprise e-commerce platforms. With its enhanced search results powered by machine-learning and natural language processing it optimizes customer experience across digital platforms.
Additional resources: Learn more about constructor.io and its offering on its official website. To know about its working, refer to its how it works page.
In this guide, we will walk you through the steps involved in setting up search capabilities on your Contentstack-powered website using Constructor.io.
Process Overview: In this guide, we have demonstrated the steps for using the collections and auto complete features of Constructor. We have created a content type in Contentstack that has all product's details. The same products get reflected in the Constructor dashboard.
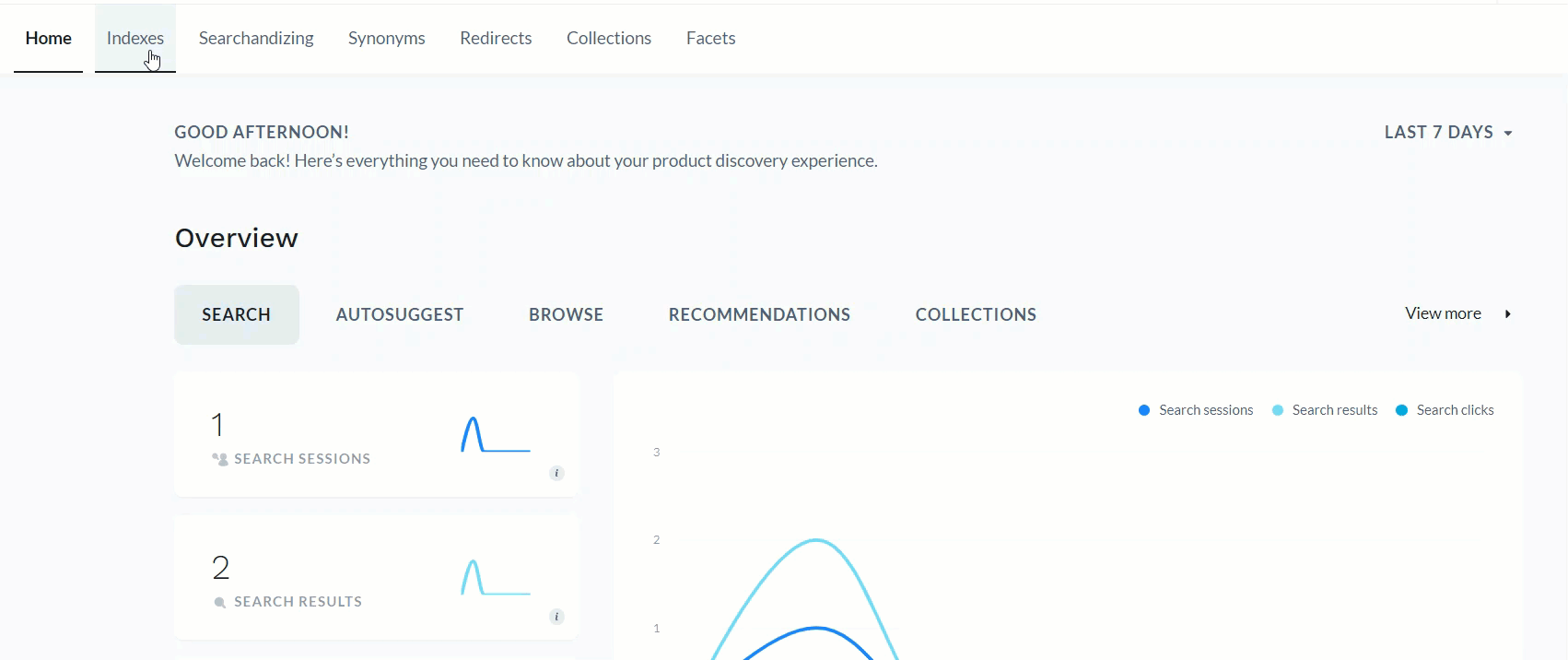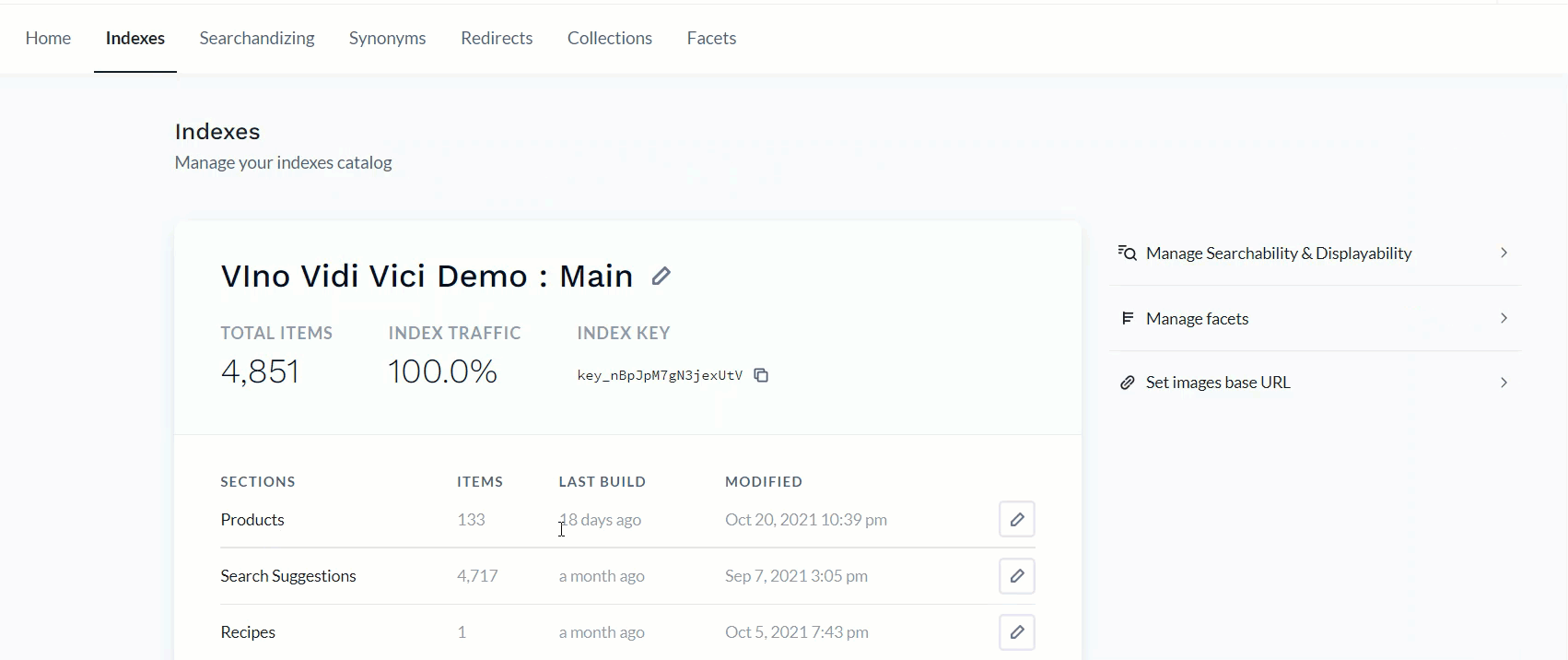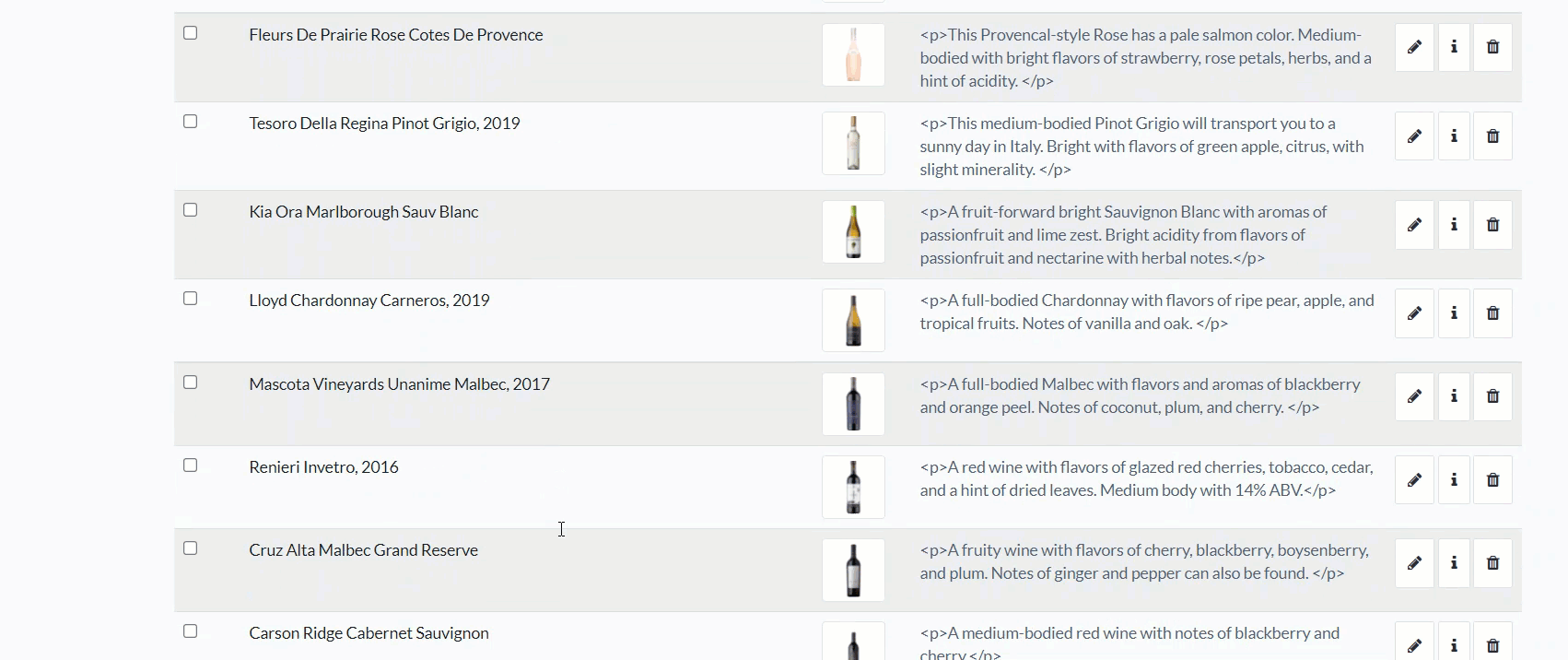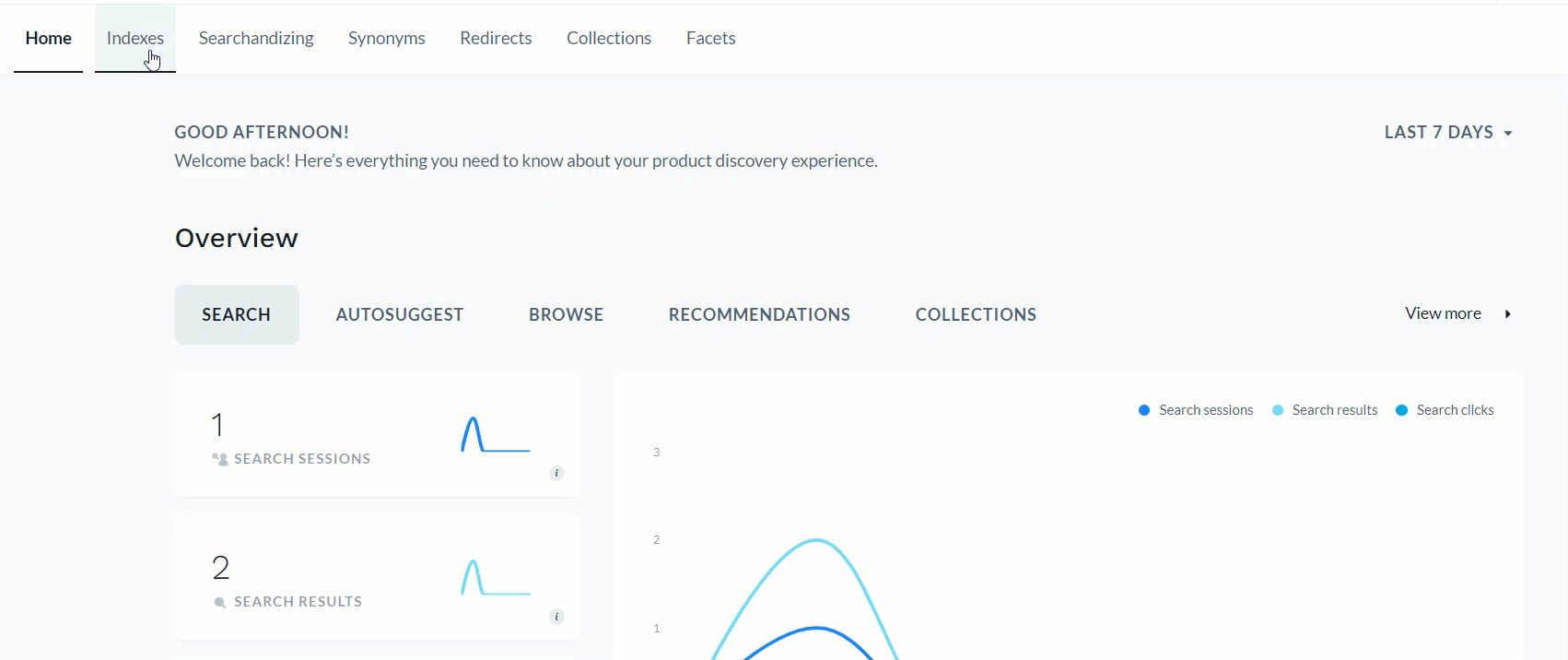
Collection is a term in Constructor.io, and is directly created in the Constructor.io dashboard which consumes the products reflected in Constructor.io from Contentstack. When any changes are made to the products in Contentstack, the same gets reflected in the Constructor dashboard.
For this exercise, we have assumed that you already have a working Constructor account with you. If you haven't created an account yet, visit the official website and sign up with one of their plans.
Now that you have the account ready, we will need the Constructor API token so that we can use its API integration features. To do this, follow the steps given below:

Now that we have the tokens handy, let's discuss the steps to configure the webhook.
Let's set up a webhook that will invoke the lambda function to execute the required operations.
Note: In your case, it will be the API gateway endpoint generated using serverless.js framework.
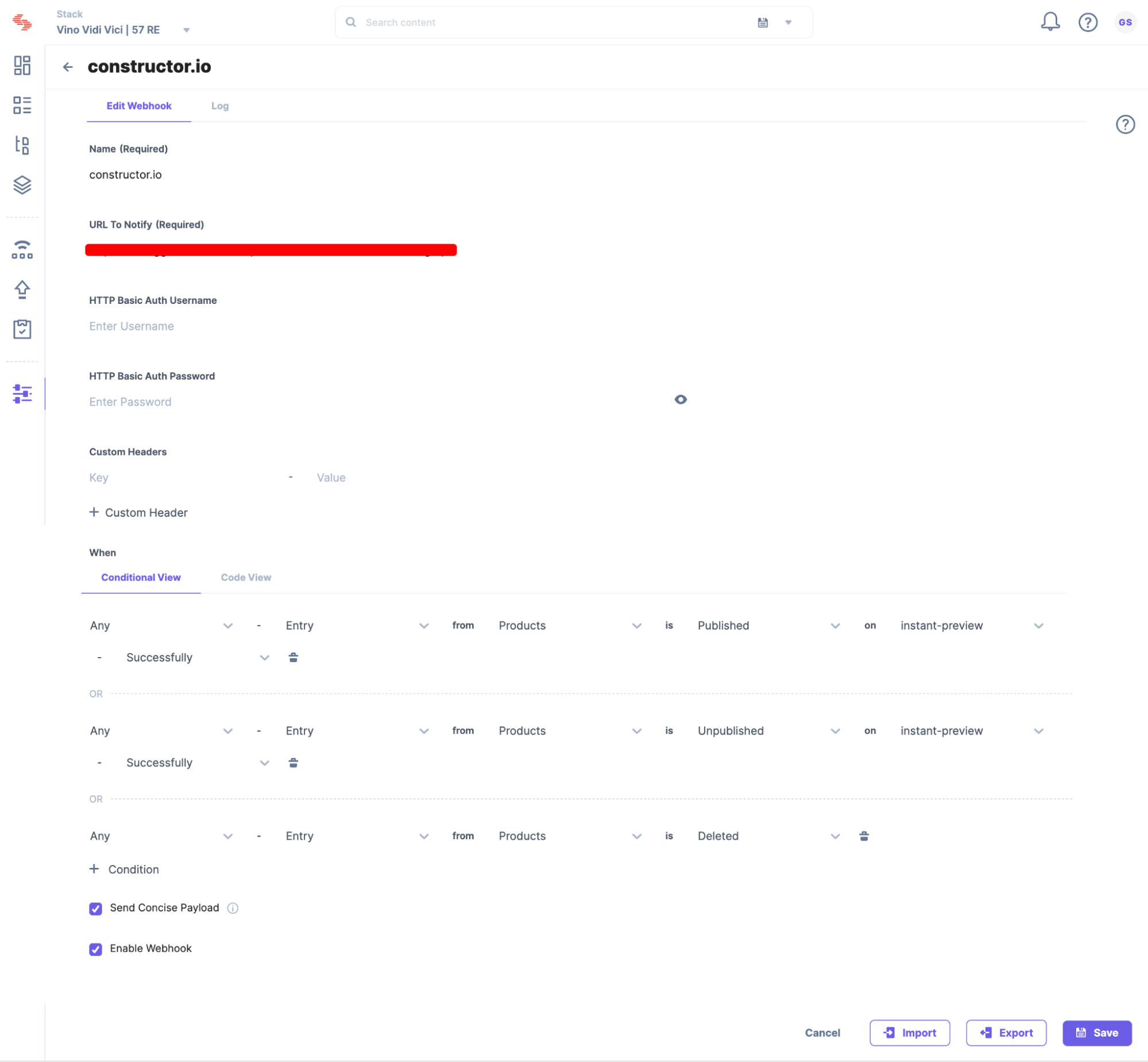
Now that we have the webhook set up ready, let's move ahead and create collections in Constructor.
In Constructor, you can create landing pages that are based on manual lists or automated rules of products by using Collections. This helps you to enhance search and browse and product discovery experience.
To create a collection in Constructor, follow the steps given below:
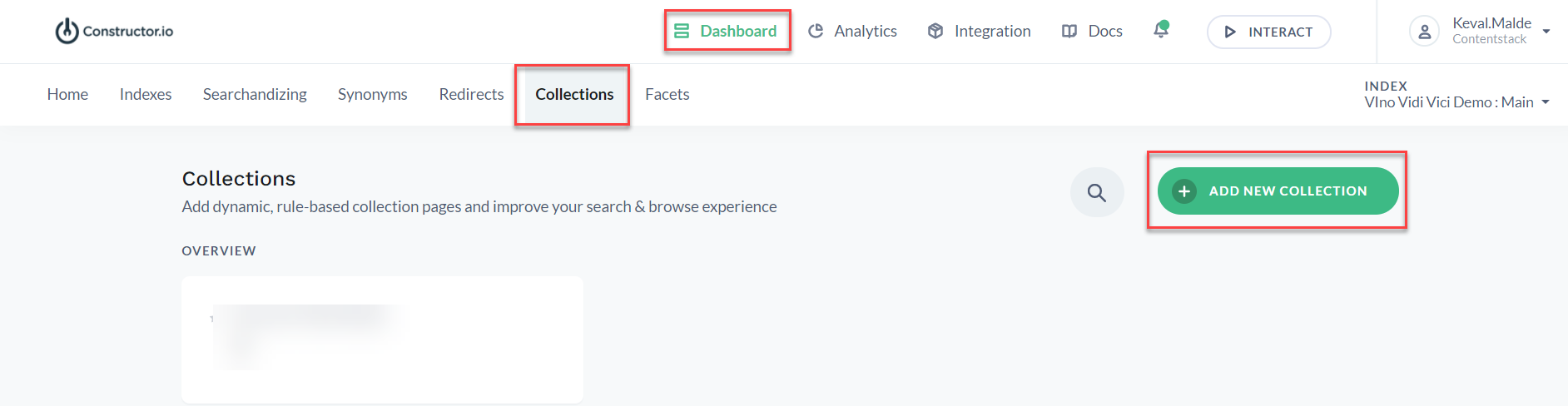
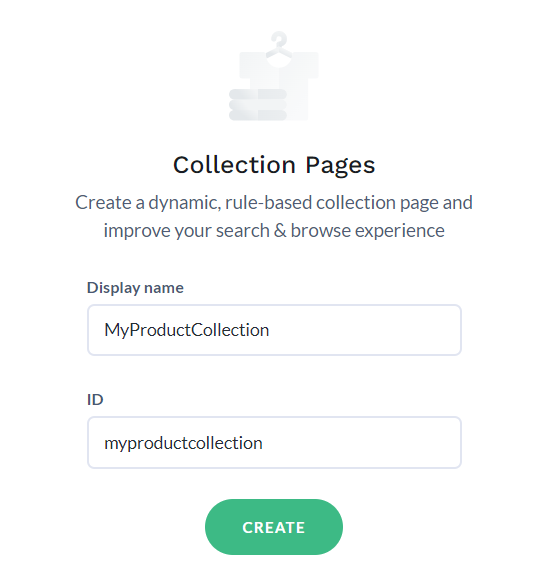
Note: The ID field gets filled automatically as you type the Display name. However, you can edit the ID if required.
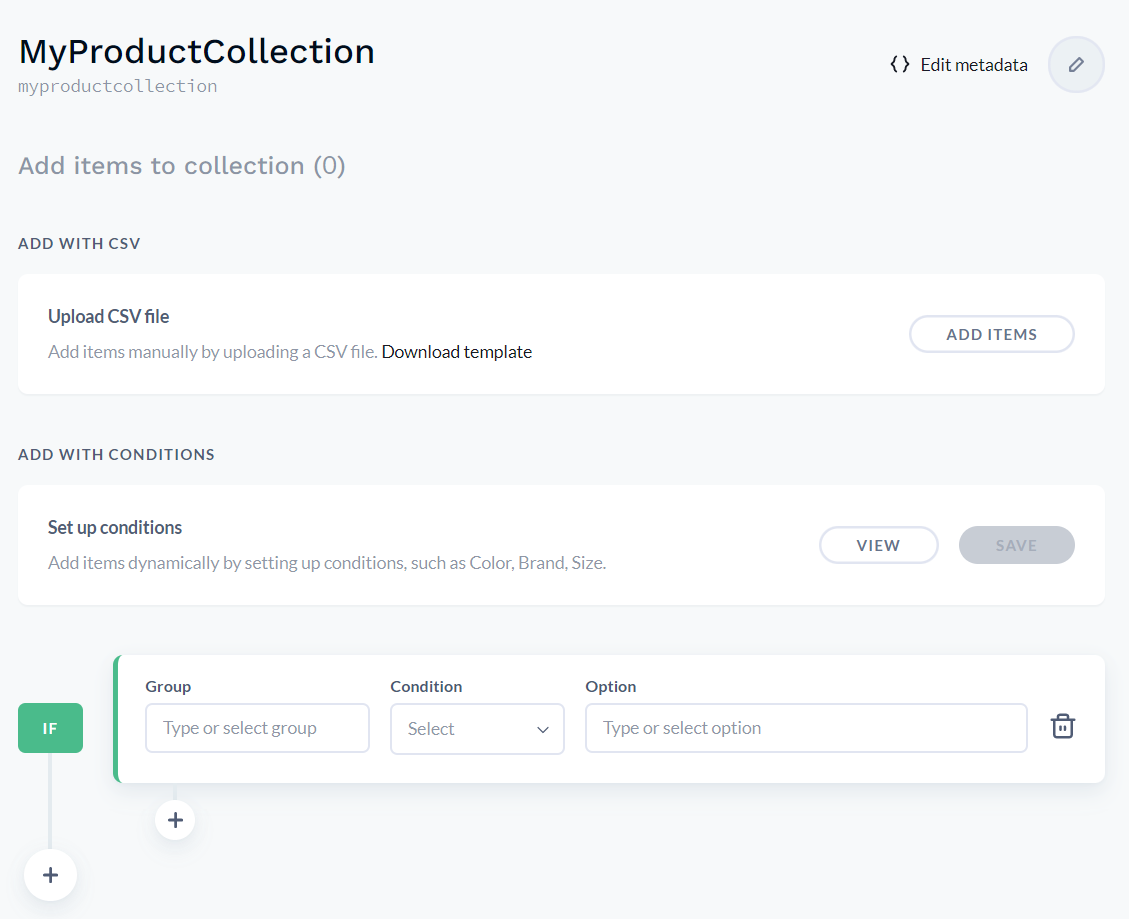
For this exercise, we have created a few collections. One of them is Weekly Wines Special, as shown below:
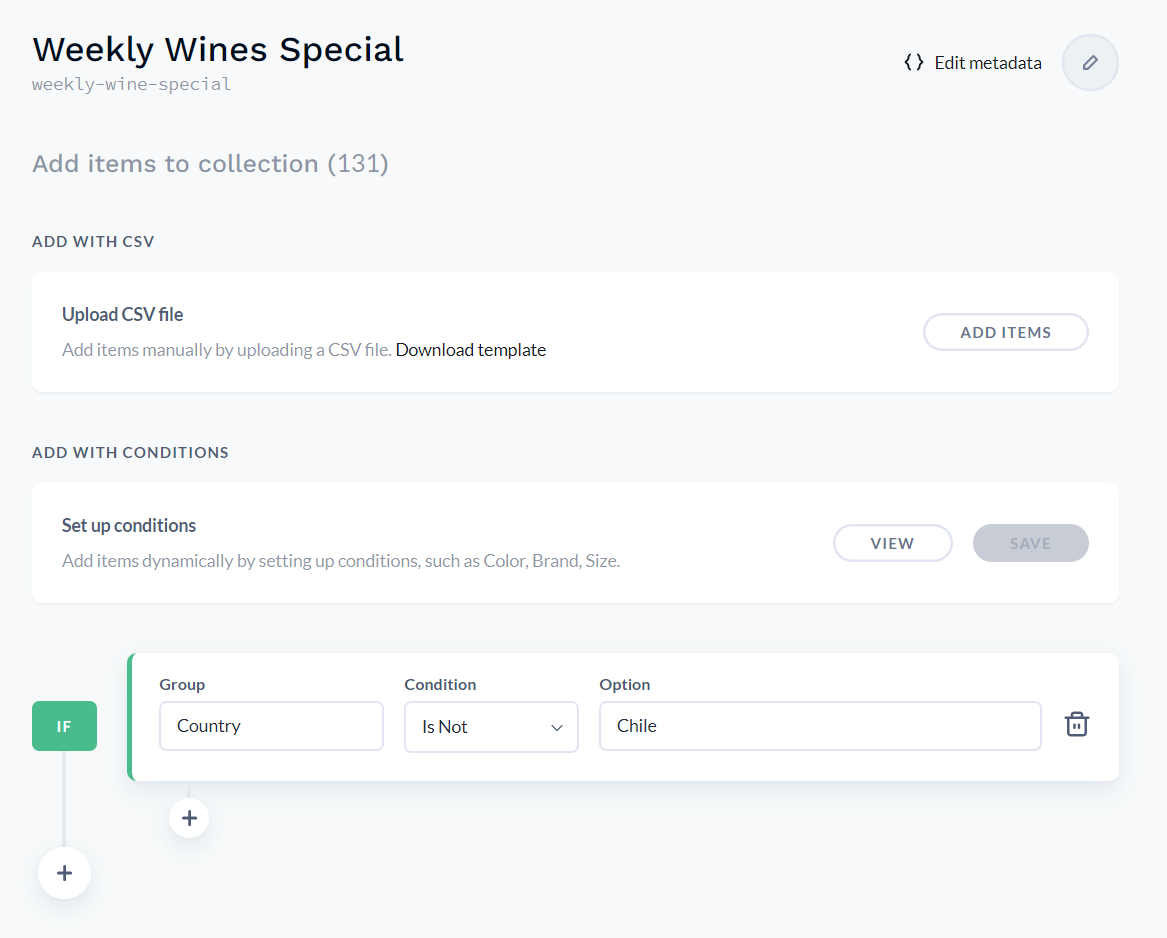
In the above condition, we have specified to list products that do not belong to the Country Chile. So based on this condition, if we click on VIEW, the following products pops up:
Similarly, you can create additional collections as required. Let's now create an extension that will be used within the modular block.
To set up the extension, log in to your Contentstack account and proceed with the following steps:

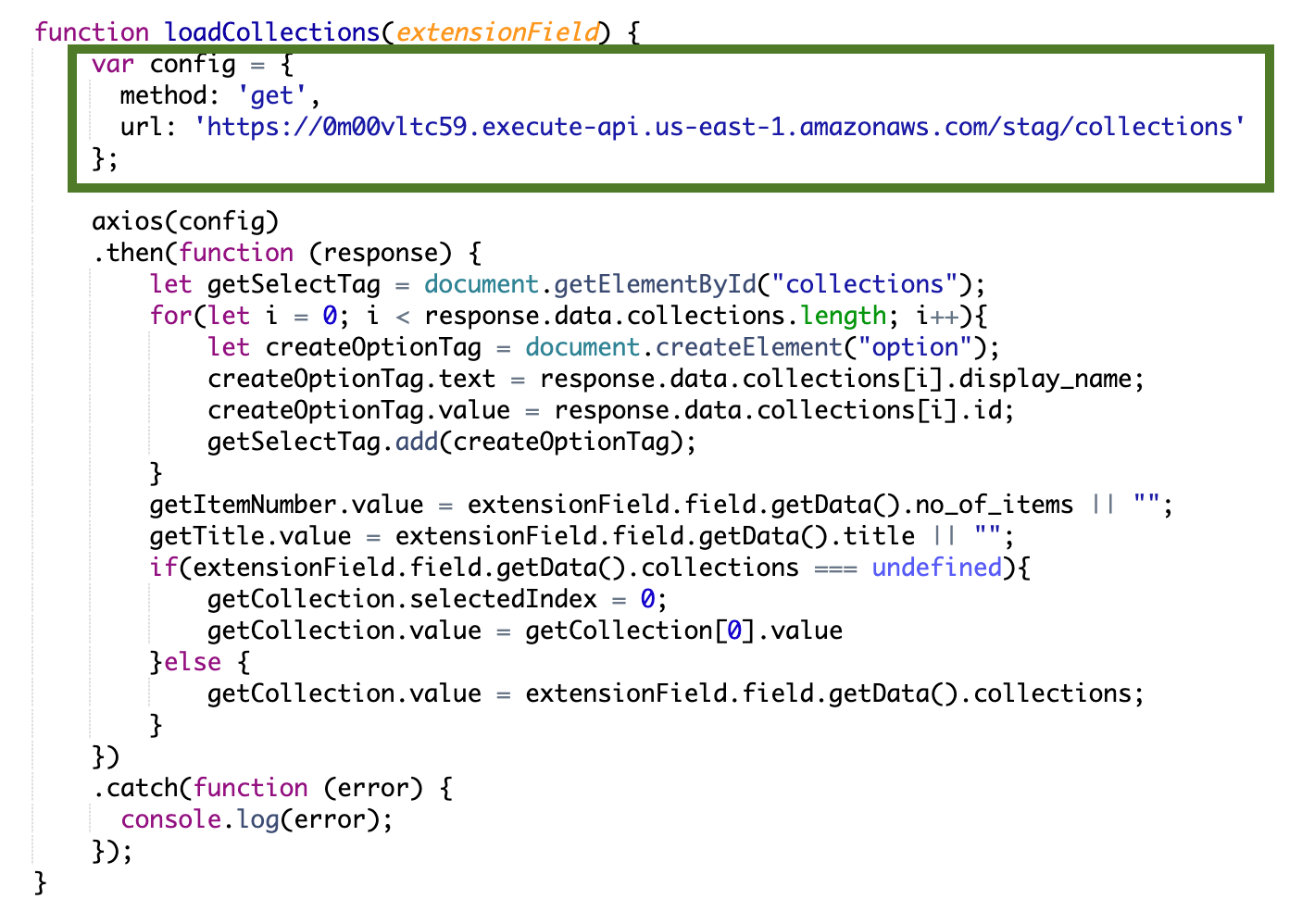
The following is the pictorial representation of the code that we have used as extension source code showing the "Consumption of AWS API endpoint" for fetching ‘List of Collections’:
Now that we have the extension ready, let's move ahead and understand how to set up the collections feature in Contentstack.
The product list that you see above in Constructor is actually fetched from Contentstack. All your products are managed at the Contentstack end and accordingly they are displayed in Constructor.
To integrate Constructor.io Collection with Contentstack, we have created a content type named Home that has the following structure:
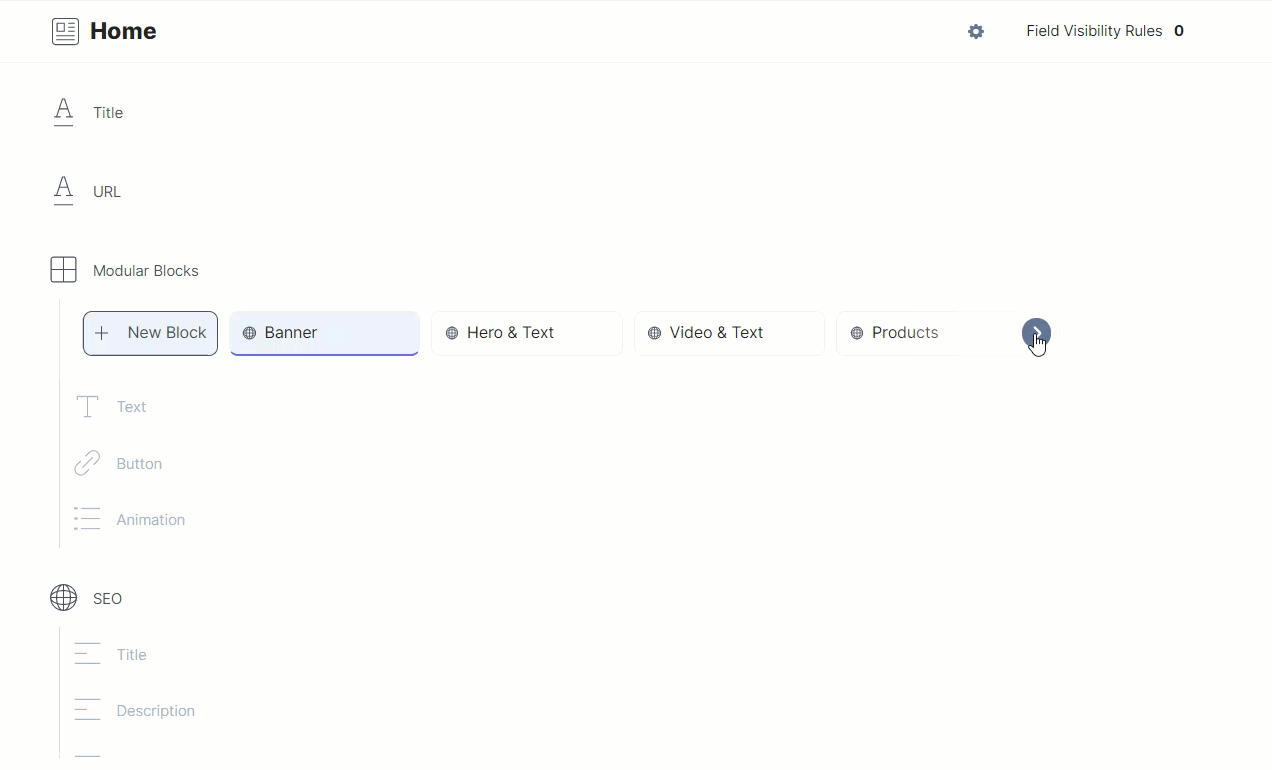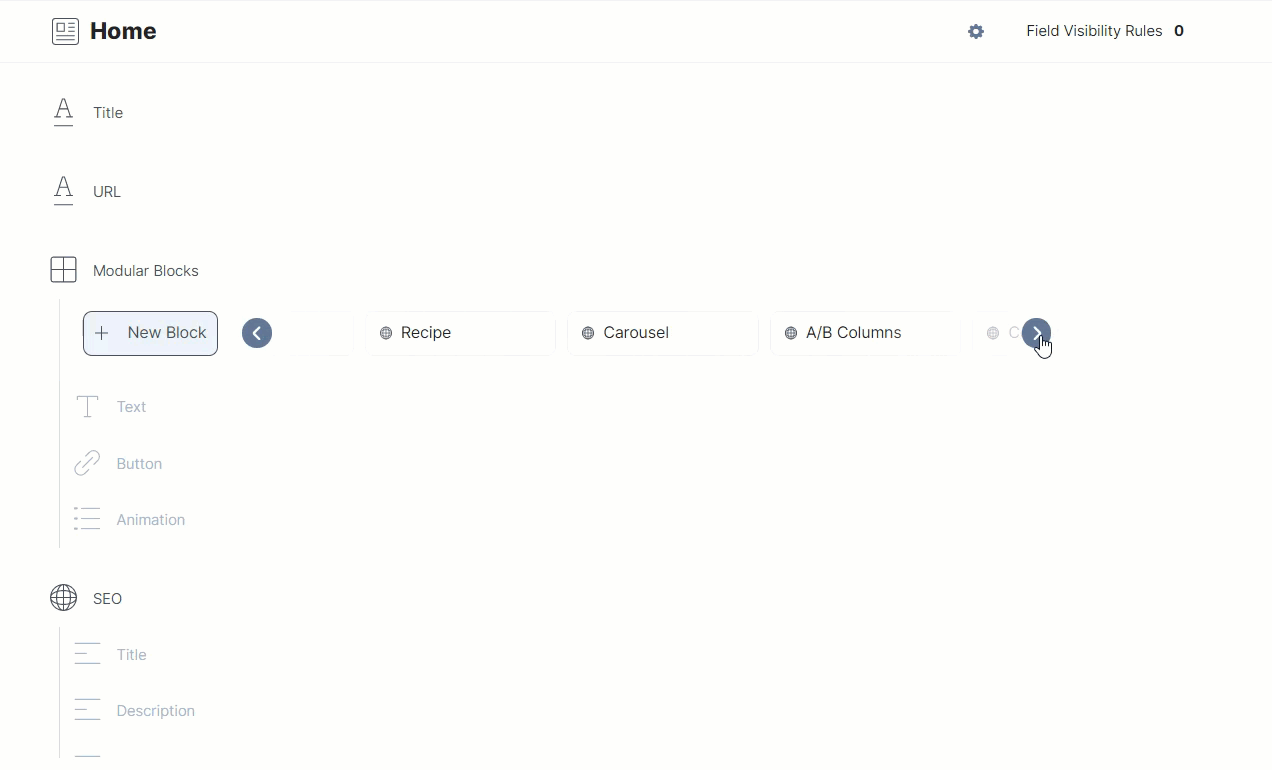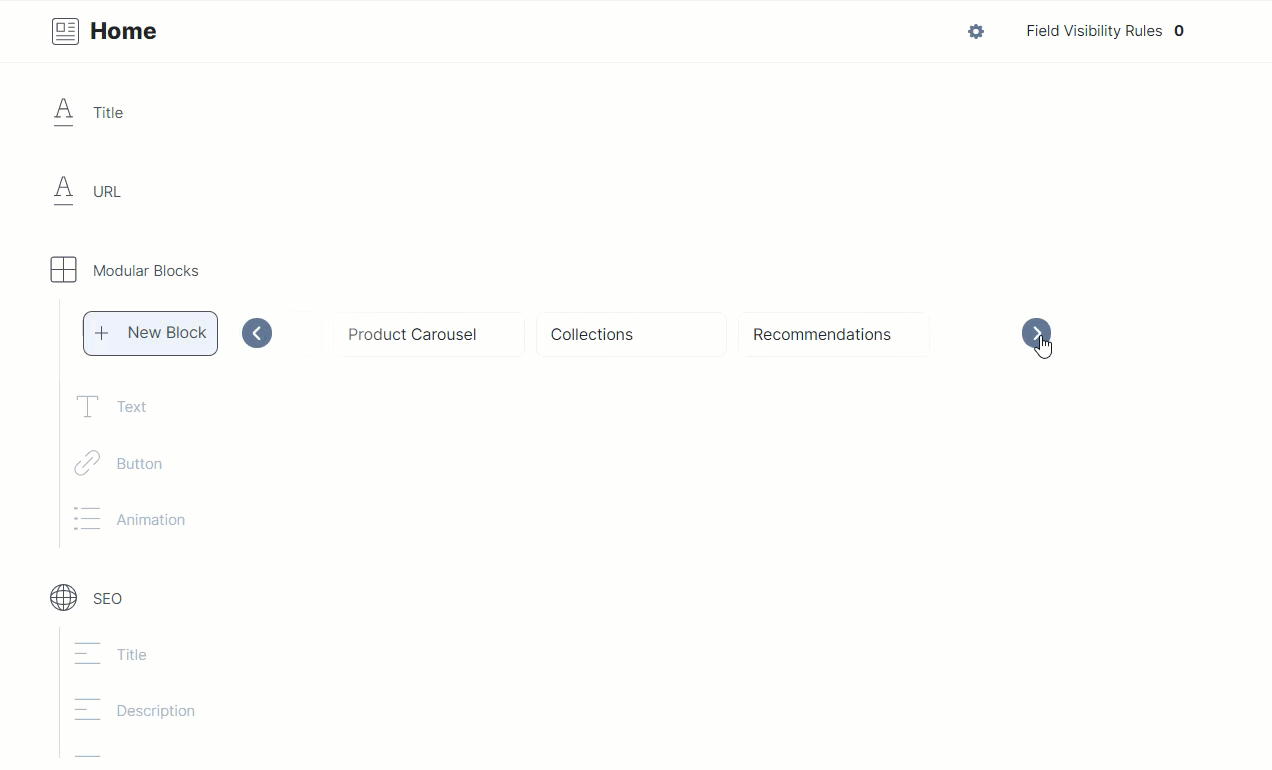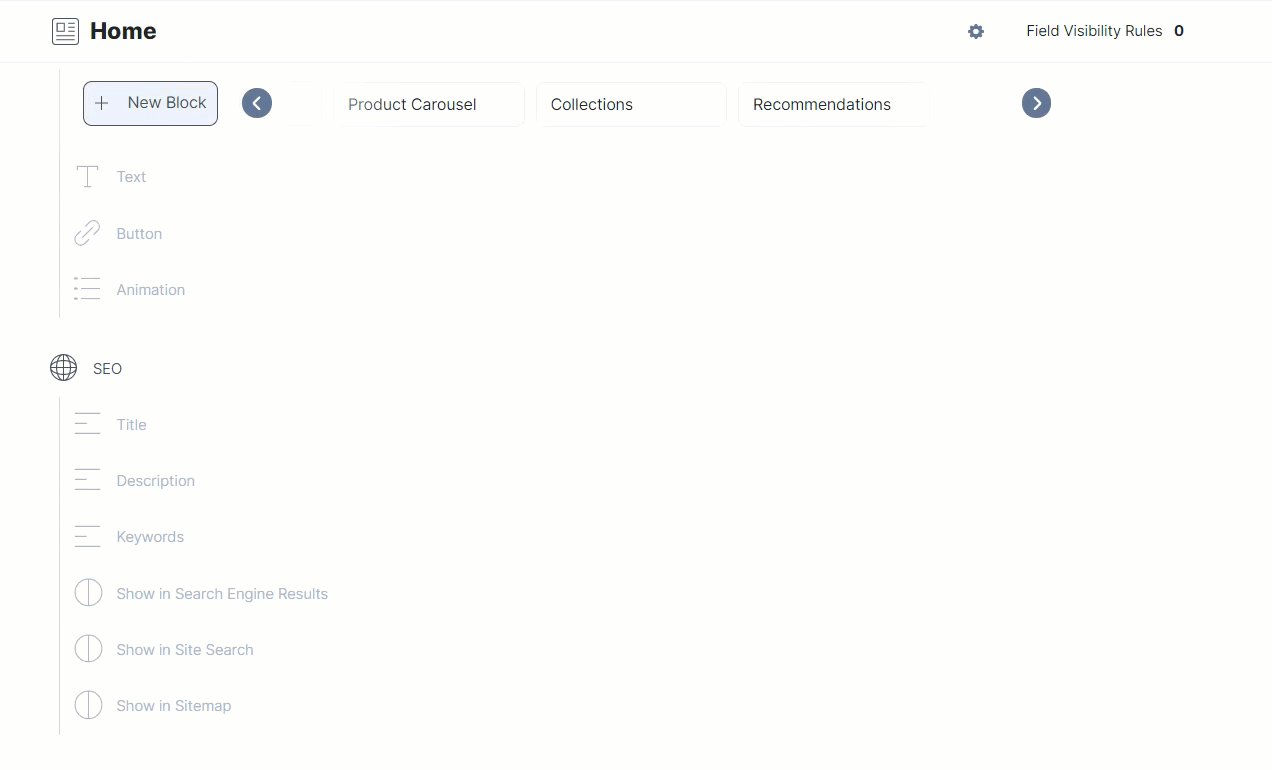
As you can see above, the content type consists of a Title field, a URL field, a Modular Block field with several fields inside it, and a Global field.
The entry of this Home content type is shown below:
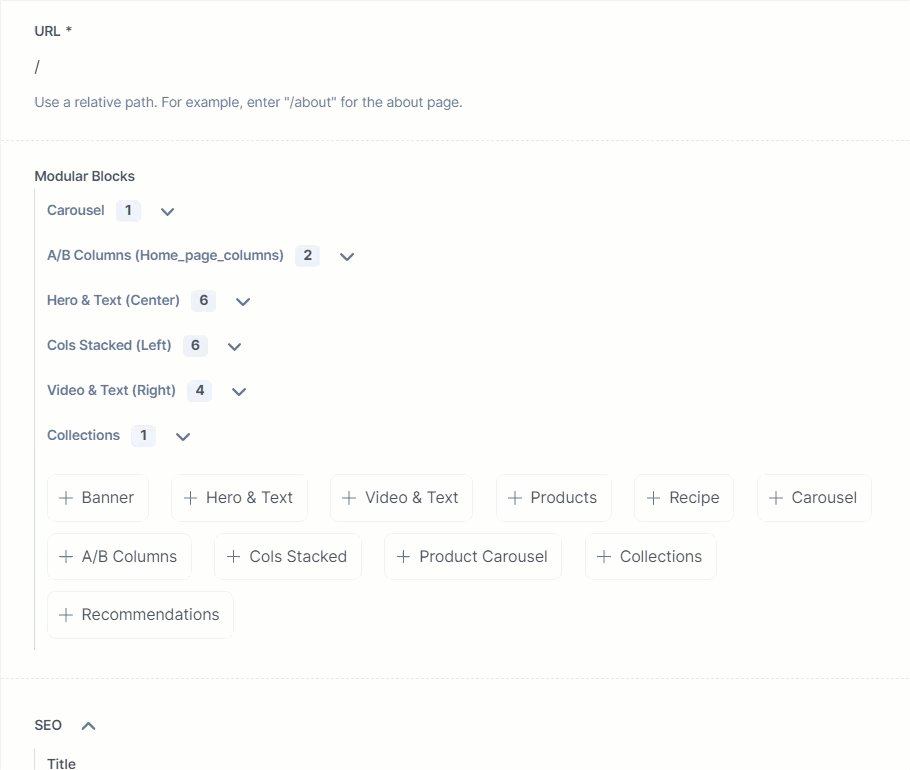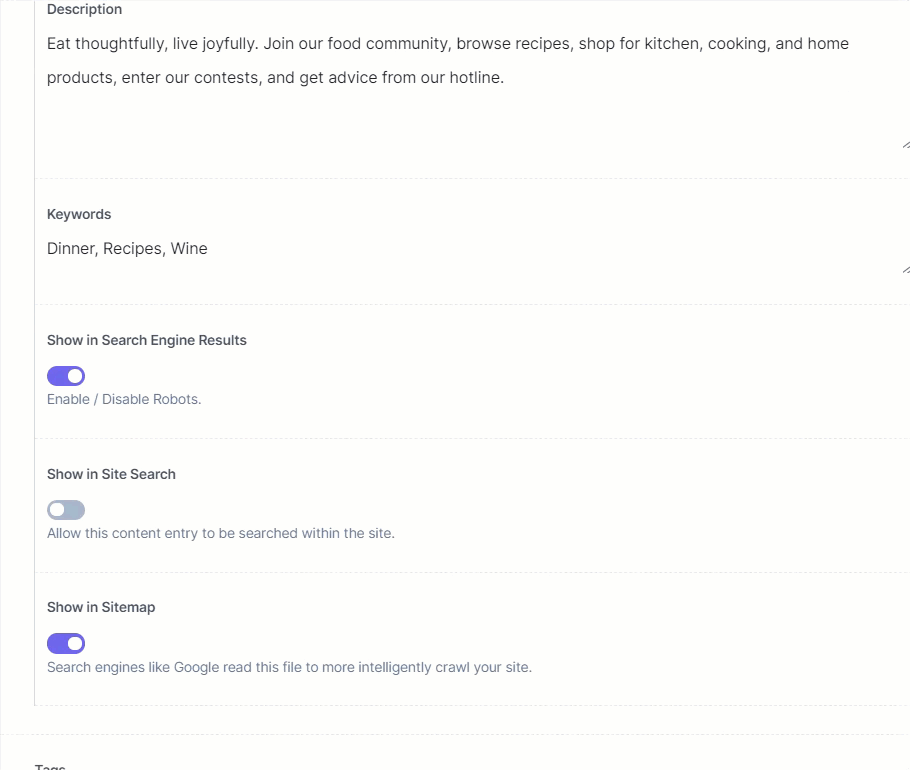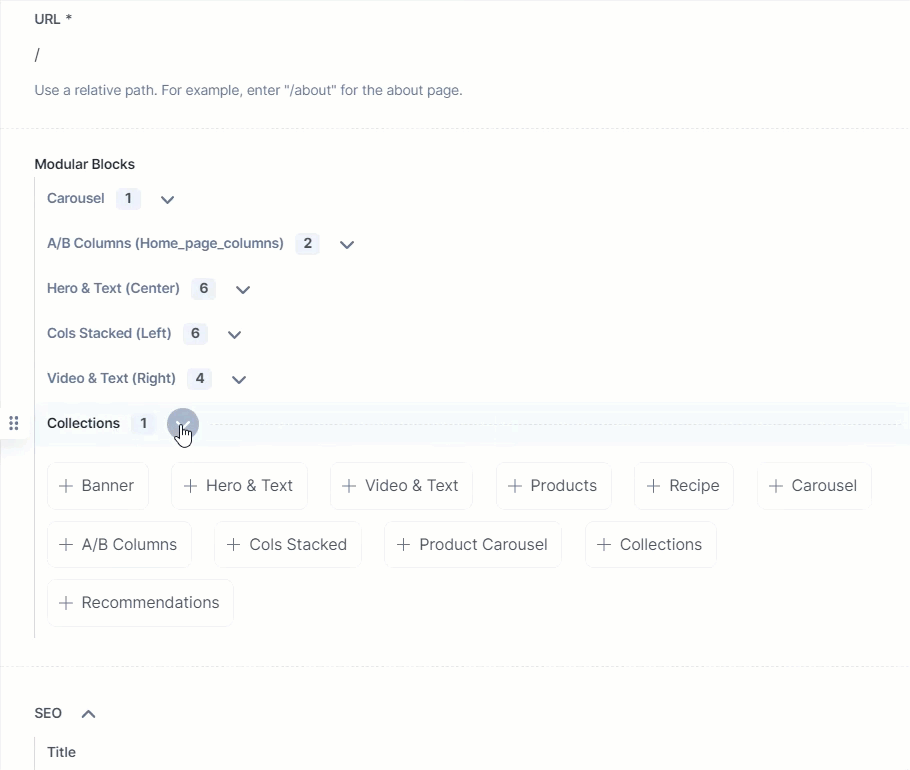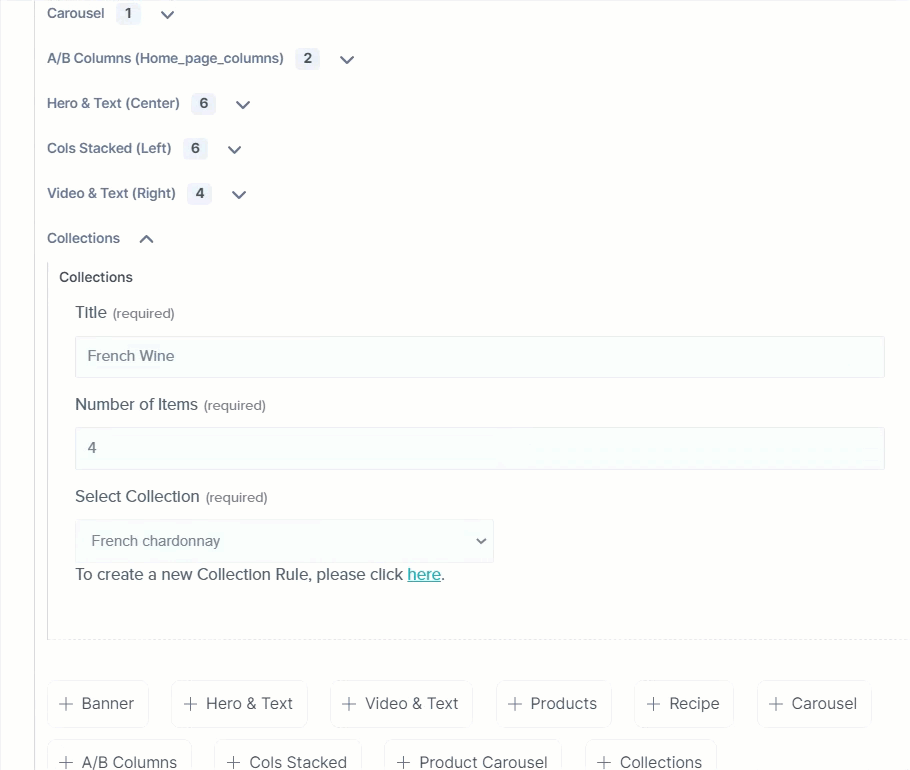
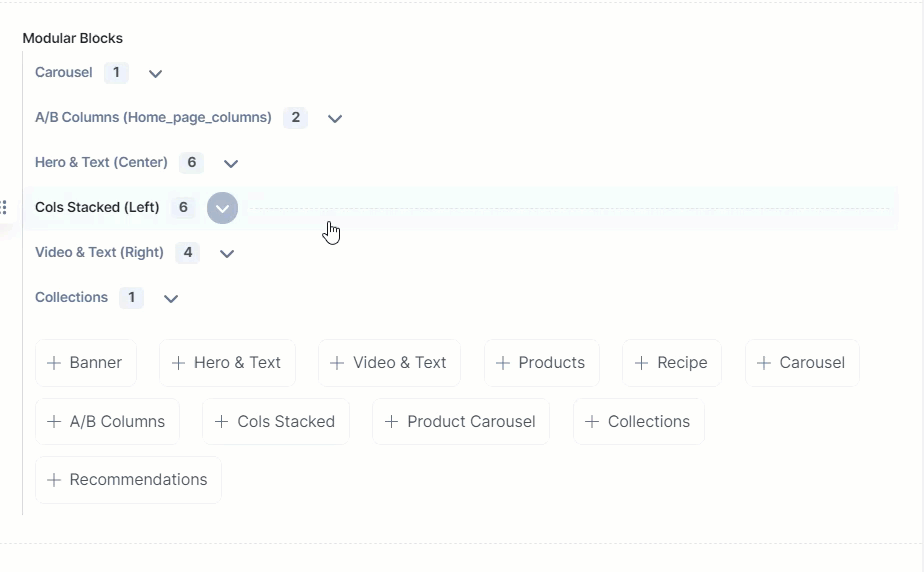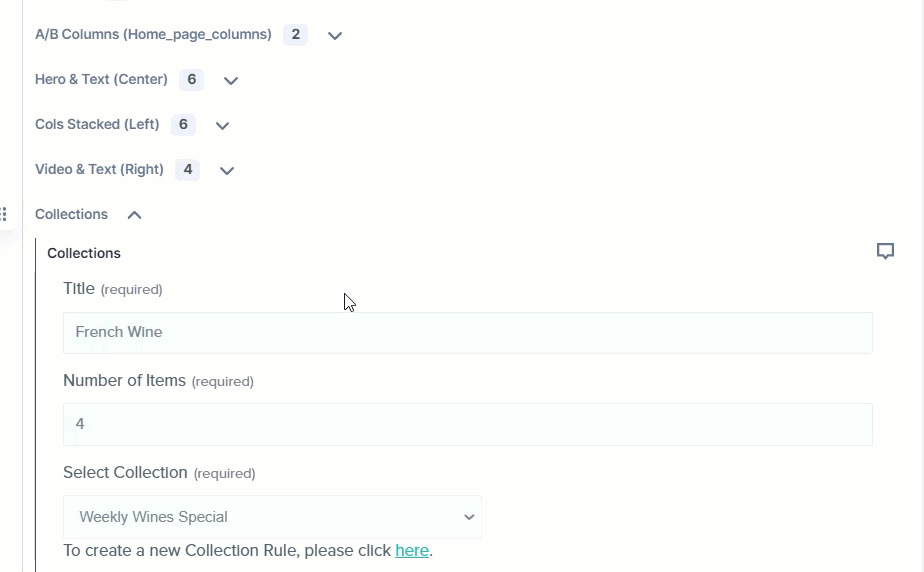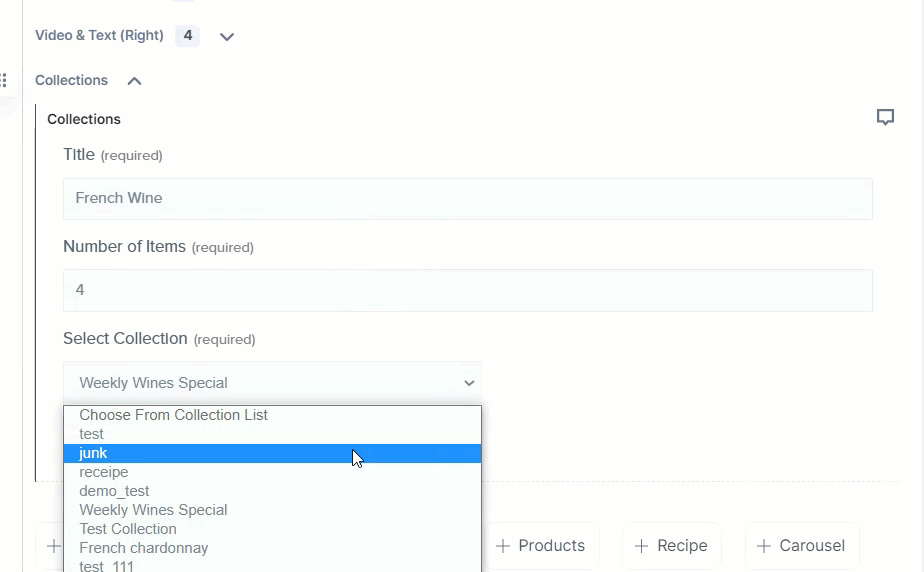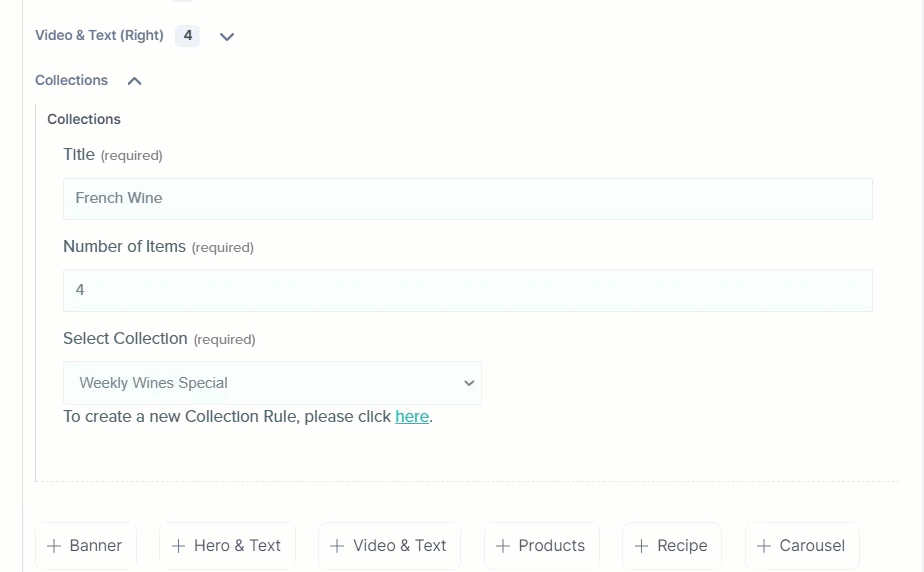
As seen above, the Modular Block field has a block named Collections (which is an extension) that contains the following fields:
If the collection you are searching for is not available in the list, you can create a new one by clicking on the ‘link’ at the bottom of this extension as shown below:
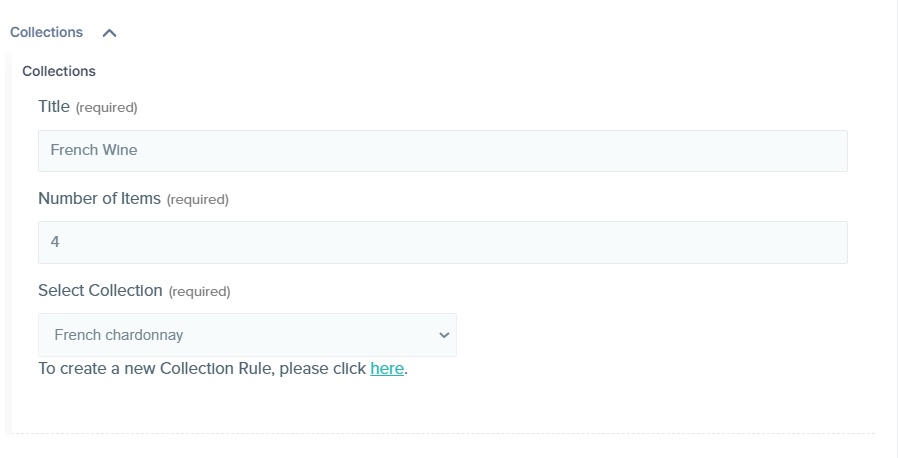
Let's now set up the extension in Contentstack
We have created the serverless to serve the Constructor.io Collections API endpoint in AWS. The AWS endpoint fetches the "List of Collections" using the Collections API from Constructor.io.
Below is the snippet of "API Call Routes Setup" in serverless for "Constructor.io Collections API":
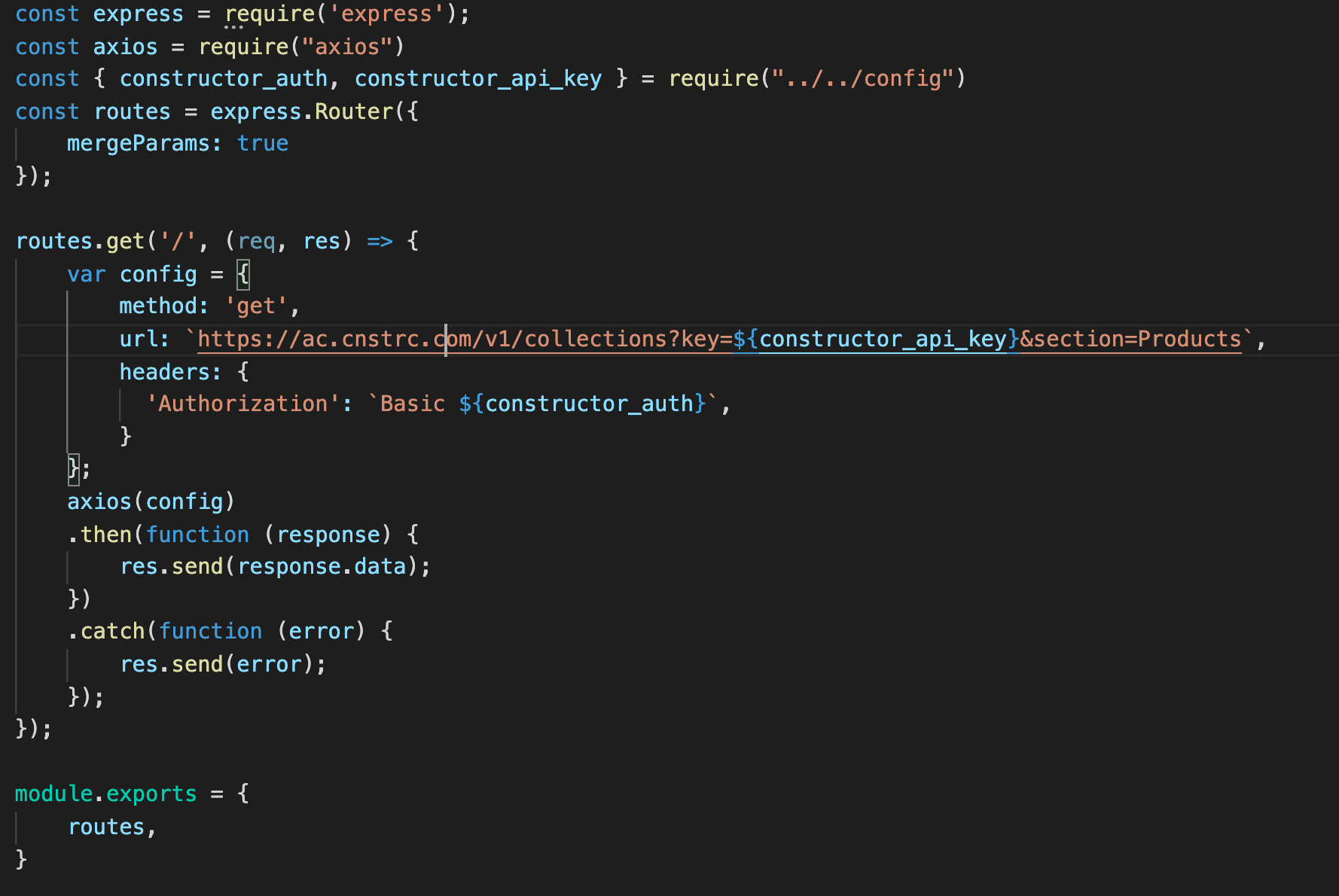
In the above code snippet, the url key has the following value:
https://ac.cnstrc.com/v1/collections?key=${constructor_api_key}§ion=Products
Where, constructor_api_key Is the API key of your Constructor.io account we created in step 1.
We have created a demo website for the example. We have created the "Collections Extension" and added it to the schema of the required content type in Contentstack. For this example, we have added it to the Home content type.
Inside the demo site, we have added a code set up to fetch the items/data for that particular collection. The code makes use of the Constructor.io Node package along with API Key to initialize the Constructor.io object.
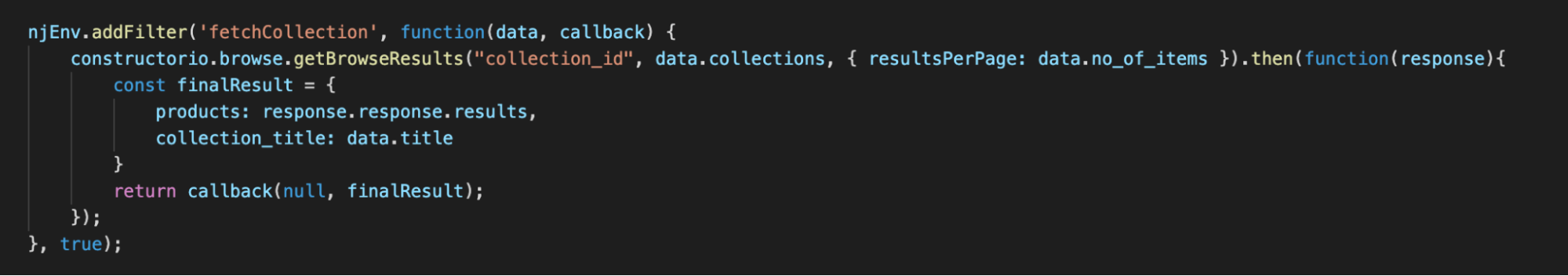
This object contains the browse.getBrowseResults() method which consumes the Collection Id that we received from Collection Extension and fetches the items/data. The following is the pictorial representation of the code for this integration. We have created a ‘Nunjucks Filter’ to integrate the API with frontend nunjucks:
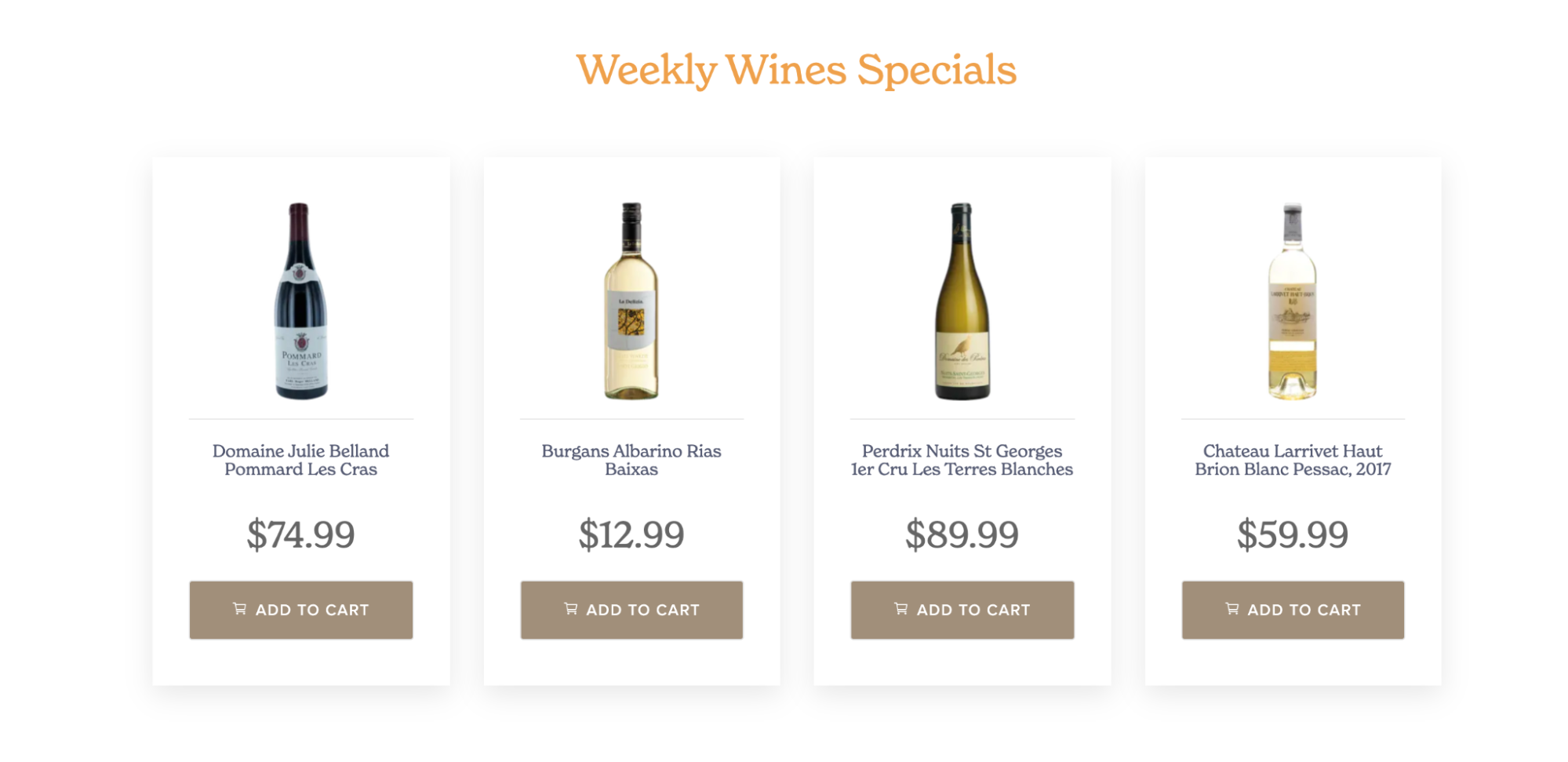
Below is the pictorial representation of the "Collections" on the demo site. Here, we have selected the "Weekly Wines Specials" (we discussed above) collection from the extension:
You can select other collections simply from the Collections extension and publish the entry.
Now that we have seen how to set up the collection in Contentstack and use the feature in Constructor, it's time to move ahead and understand how to implement the auto-complete feature.
To implement the auto-complete feature, you can use any of the methods as discussed below.
To install with jQuery, use the following code snippet:
<script type="text/javascript">
$.getScript("//cnstrc.com/js/cust/<your_custom_bundle_name>.js", function () {
$("#query").constructorAutocomplete({
key: "<your_api_key>",
});
});
</script>In the above example, #query is the DOM selector of your search box and <your_api_key> can be found on your dashboard as discussed in step 1. Also for the <your_custom_bundle_name>.js, get in touch with the Constructor.io support team.
To install using HTML/JavaScript, use the following code snippet:
<script
type="text/javascript"
src="https://cnstrc.com/js/cust/<your_custom_bundle_name>.js"></script>
<script>
const inputElement = document.querySelector("#query");
const autocomplete = new ConstructorioAutocomplete(inputElement, {
key: "<your_api_key",
});
</script> Additional resource: For more information, refer to these links: autosuggest_client, autosuggest client installation, autosuggest client methods, and autosuggest client advanced options.
To integrate Constructor.io Search page with Contentstack, use the following steps:
npm i @constructor-io/constructorio-node
Note: This library should only be used in a server-side context.
const ConstructorIOClient = require('@constructor-io/constructorio-node');
var constructorio = new ConstructorIOClient({
apiKey: 'YOUR API KEY',
});
constructorio.search.getSearchResults('<search-query>', {
resultsPerPage: <result page option>, ---- this is option
filters: {
<option1 >: “ ” ,
},
});constructorio.search.getSearchResults('t-shirt', {
resultsPerPage: 40, // result page display option
filters: {
size: 'medium' // Filter option
},
});To get the complete API documentation, visit the GitHub Pages. For information, refer to the following links:
The sample app that we have developed for this example uses the webhook integration. If you want to deploy this webhook integration, the following are the requirements:
Once you have the prerequisites ready, follow these steps to deploy this project:
app: constructor-webhook
service: constructor-webhook
frameworkVersion: '2'
Provider:
name: aws
runtime: nodejs12.x
stage: stag
region: us-east-1
stackName: ${self:service}-${sls:stage}
apiName: ${self:service}-${sls:stage}
lambdaHashingVersion: 20201221
profile: constructor
deploymentPrefix: ${self:service}
Functions:
Webhook:
handler: handler.handler
Events:
- http:
path: /{proxy+}
method: any
cors: true
<strong>Note</strong>: To deploy without the dashboard, you will need to remove the org fields from the serverless.yml file.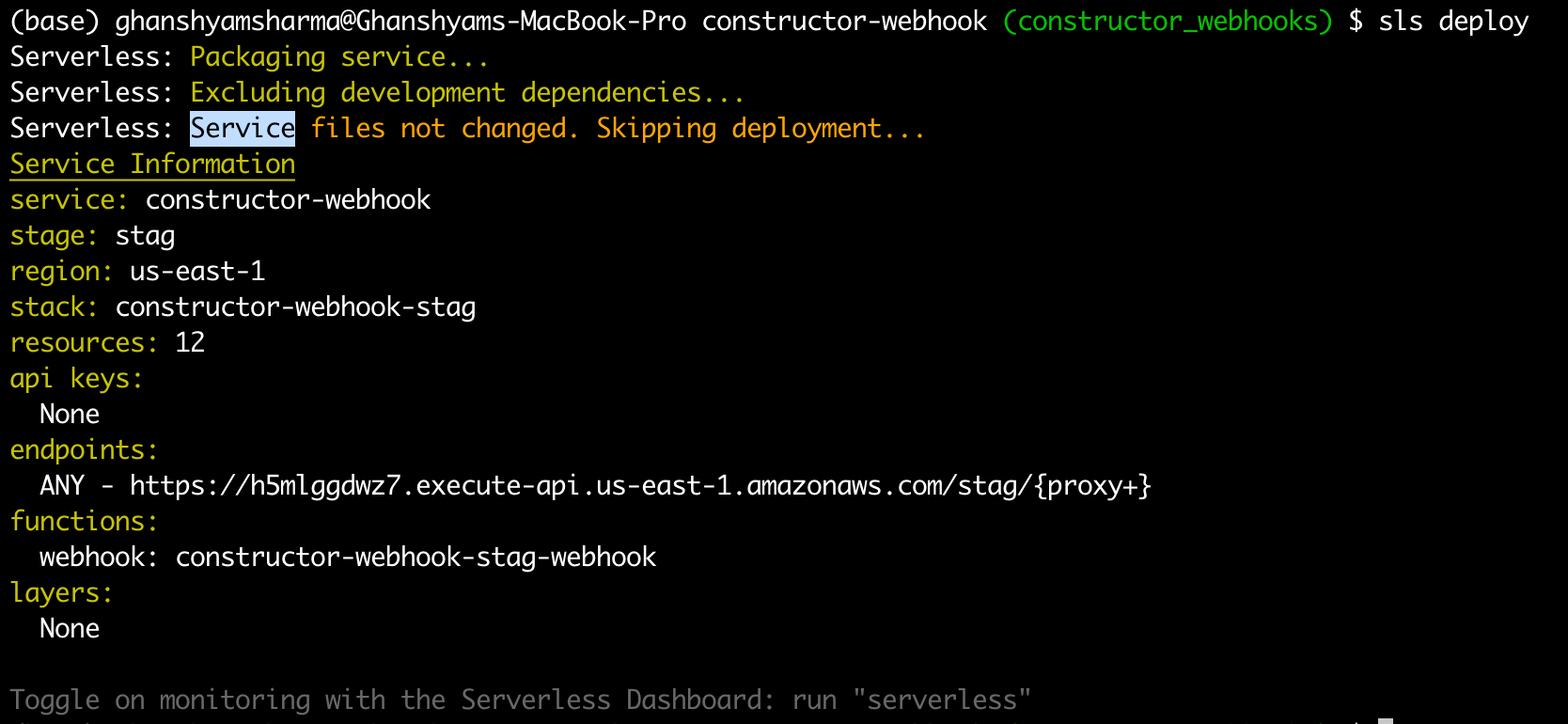
Note: In the current form, after deployment, your API is public and can be invoked by anyone. For production deployments, you might want to configure an authorizer. For details on how to do that, refer to HTTP event docs.
After the successful deployment, you can call the created application via HTTP. We have used the following endpoint for webhooks configuration:
curl https://xxxxxxx.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/stag/api
Use the steps to trigger the webhook that we created in step 2. Then follow the steps given below:
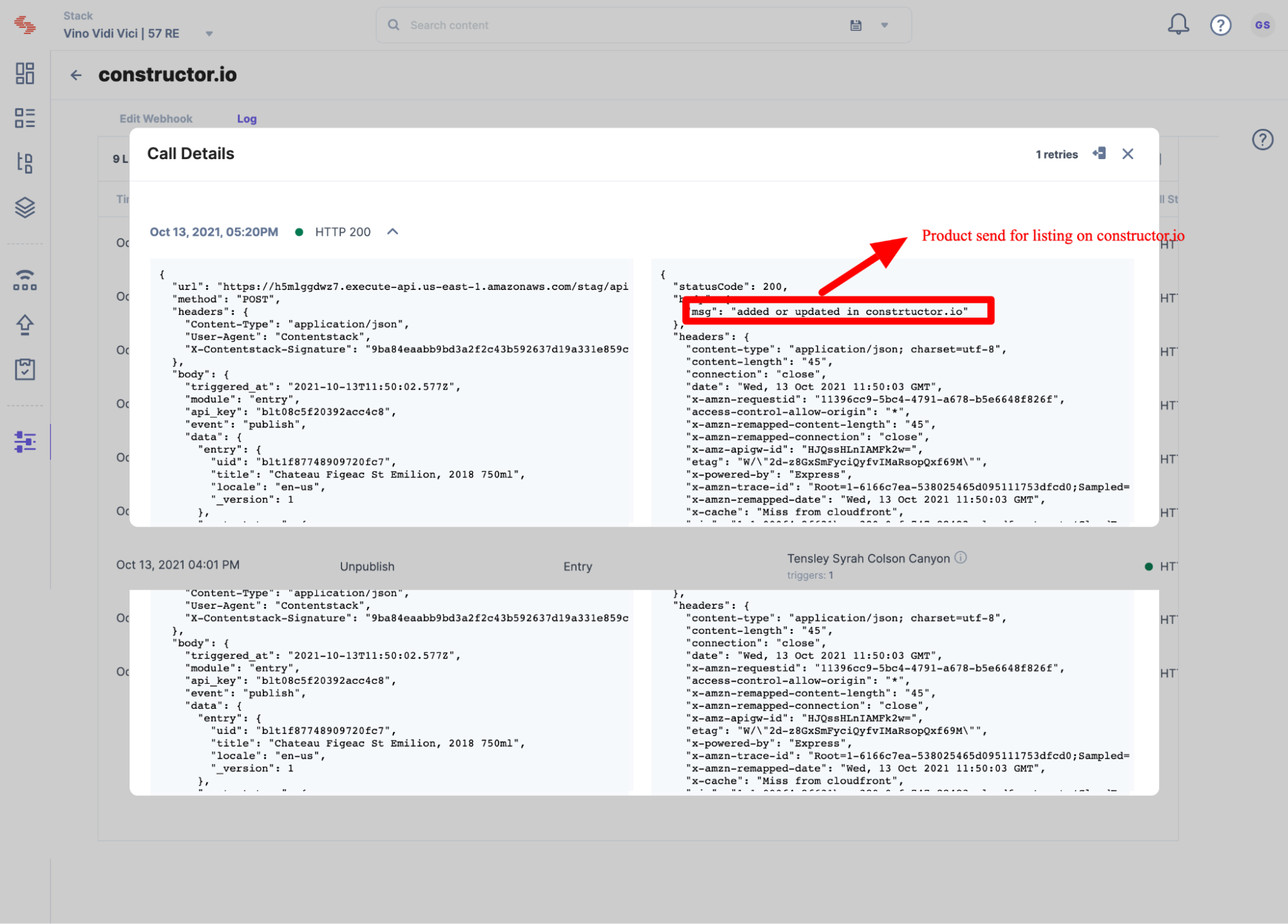
After you’ve finished working with this example, remove all resources to make sure you’re not getting billed for unused resources.
Run sls remove to remove all resources.
Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback