Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback
In the JSON Rich Text Editor, each paragraph is a block; each block is an array; each array has multiple spans of text objects, storing different nodes of text. It returns clean data, making it easier to process in the backend.
The JSON RTE is composed of Blocks that contain text within them. The schema and example for a block within the RTE is as follows:
Schema:
{
uid: { type: String, required: true },
type: { type: String, required: true },
attrs: { type: Object },
children: { type: Array[id(Block), Text] }
}
Example:
{
"type": "h1",
"uid": "3ddd280397cf44bcb8f",
"attrs": {},
"children": [
{
"text": "Hello World!",
"bold": true
},
{
"uid": "blta5aa9ca151e65333"
},
{
"text": "Welcome",
"bold": true
}
]
}
Properties of Blocks within a JSON RTE:
Note: When you update an existing JSON RTE, you need to pass the dirty attribute for each content block. Set the attribute to true.
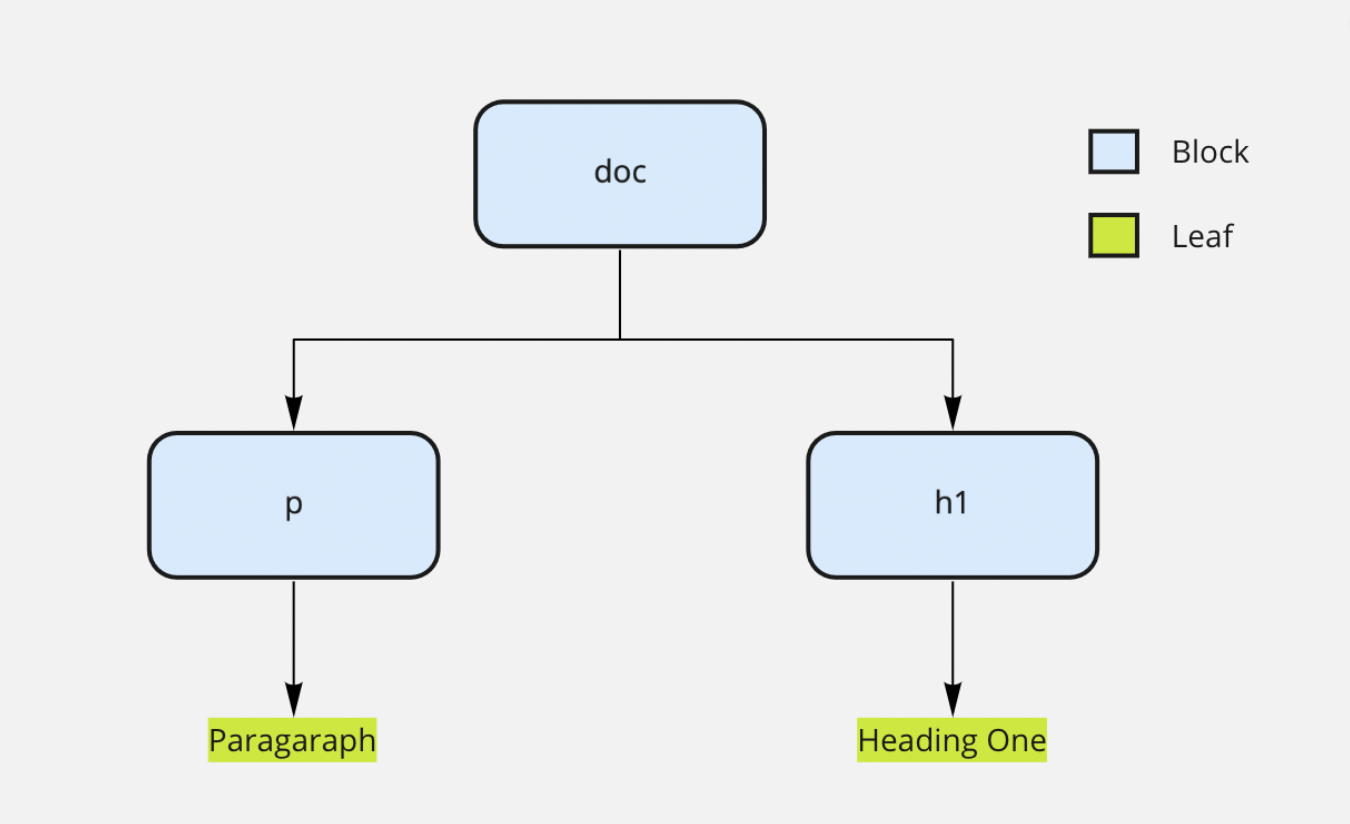
Structure of JSON Rich Text Editor
{
"type": "doc",
"children": [
{
"type": "p",
"children": [
{
"text": "Paragraph"
}
]
},
{
"type": "h1",
"children": [
{
"text": "Heading One"
}
]
}
]
}
In the JSON Rich Text Editor, the JSON structure is represented as a Node which consists of two types:
The editor content that is inside a Node of type doc acts as a root for the content. Where a Block node is a JSON structure with a “children” key in it. Whereas a Leaf node will just have “text” which may include formatting properties (mark) like “bold”, “italic”, etc.
Mark: You'll see a mark used in the below example which is nothing but a leaf property on how to render content. For example,
{
"text": "I am Bold",
"bold": true
}
Here, bold is the mark or the formatting to be applied to the "I am Bold" text.
Render Type
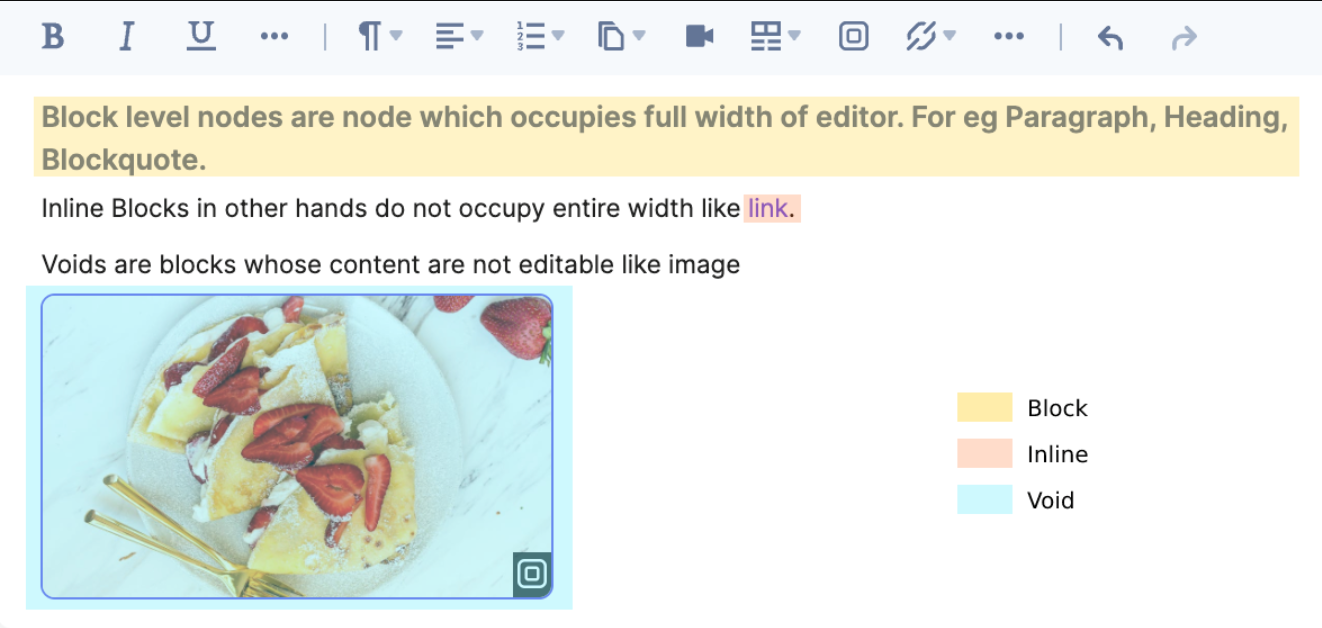
A Block node can be rendered in three different ways as follow:
Note: For more information on the requirements to work with JSON RTE, refer to Prerequisites.
Additional Resource: You can read more about the schema of the JSON RTE in our documentation where we have covered it extensively.
Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback