Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback
https://cdn.contentstack.io/https://eu-cdn.contentstack.com/https://azure-na-cdn.contentstack.com/This document is a detailed reference to Contentstack’s Content Delivery API.
The Content Delivery API is used to retrieve content from your Contentstack account and deliver it to your web or mobile properties. If you are looking for APIs to manage content, you should use the Content Management API
Our APIs serve content via a powerful and robust content delivery network (CDN). Multiple datacenters around the world store a cached copy of your content. When a page request is made, the content is delivered to the user from the nearest server. This greatly accelerates content delivery and reduces latency.
Warning: The Content Delivery API (CDA), available at cdn.contentstack.io, should be used to only fetch content from Contentstack. We recommend users to NOT use this endpoint for any other content management activities, because all content management activities using this endpoint will be blocked soon.
We have partnered with Fastly as our CDN. It has powerful points of presence (POPs), strategically placed in the highest density internet exchange points across the world. Our CDN has close to 100 POPs and is adding new ones all the time.
Warning: We only support version 3 on the CDN. If you're still using version 2 (which we recommend you should not), switch to the CDN version for even faster loading. And, we have a URL size limitation of 8KB on API Requests that hit our CDN services. Any Request URL that goes above this size limit will receive the 400 - Bad request error response. Please make sure you limit the size of your API Requests.
We have created SDKs, API references, getting started guides, and sample apps for some of the popular languages and platforms. You can use them to build your own apps and fetch content from Contentstack.
Contentstack SDKs let you interact with the Content Delivery APIs and retrieve content from Contentstack. They are read-only in nature. The SDKs fetch and deliver content from the nearest server via Fastly, our powerful and robust CDN.
You will find a list of all the available SDKs under the Development Resources and SDKs section.
We provide SDKs for the following platforms:
The process for building sample apps and working with the SDKs differ based on the platform. We have covered them in detail in their respective sections.
Since the Content Delivery APIs (CDAs) are private APIs, you will need to pass the following as HTTP headers to make authorized CDA requests:
access_token key)The API Key is a unique key assigned to each stack. The Delivery Token is a read-only credential that you can create for different environments of your stack.
While Content Delivery API requests may work with Access Token (instead of Delivery Token), we strongly recommend that you not use it, since we have already deprecated Access Token for new stacks.
Note: The nomenclature for the use of delivery tokens in CDA requests will remain the same, i.e. you need to pass the value of the delivery token against the access_token key.
For stacks that are part of organizations created after June 24, 2020:
access_token key.api_key (Stack API key), access_token (access token of the stack), authtoken (user generated authtoken), and authorization (management token of the stack) as query parameters for any stack-specific API requests.Note: We have deprecated the usage of Access Tokens for all stacks. We strongly recommend that you use Delivery Tokens for fetching published content via the Content Delivery API and Management Tokens for fetching draft content via the Content Management API.
To retrieve the stack API key and the delivery token of a specific publishing environment of your stack, perform the steps given below after logging into your Contentstack account:
Additional Resource: Read more about how you can create a new delivery token.
Note: Only the stack owners, developers, and admin can create delivery tokens.
The rate limit is the maximum number of requests that you can make using Contentstack’s API in a given period. There are no limits on the requests that you make to the cached data on Contentstack’s CDN. Contentstack's API automates caching to enable our API to scale. For uncached requests, i.e., requests to the origin server, there is a maximum limit of 100 requests per second per organization. The rate limit depends on your plan, and you can request an increase in your rate limit if necessary.
cdn.contentstack.io/v3/endpoint.HTTP headers let the client and the server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response. An HTTP header consists of its case-insensitive name followed by a colon (:), then by its value.
Here’s what an HTTP response body looks like:
< x-served-by: cache-lax8631-LAX, cache-bur17525-BUR < x-cache: MISS, HIT < x-cache-hits: 0, 1 < x-runtime: 27ms < age: 5182 < x-timer: S1557441707.643683,VS0,VE0
Let’s understand what the above HTTP Header means:
x-served-by: cache-lax8631-LAX, cache-bur17525-BURTwo cache-nodes in X-Served-By show that shielding is turned on, with
cache-lax8631-LAX serving as the delivering cache node at the "shield" datacenter and cache-bur17525-BUR serving as the delivering cache node at the "local" datacenter.
< x-cache: MISS, HITThe X-Cache: MISS, HIT indicates that the requested object was not in the shield cache (a MISS) but was in the local delivering node (a HIT). For more details, refer Understanding cache HIT and MISS headers with shielded services.
< x-cache-hits: 0, 1The X-Cache-Hits reflects that same “MISS, HIT” information in numeric format as
0, 1.
< x-runtime: 27msThe X-Runtime HTTP response header provides the time (in milliseconds) an application takes to process a request.
< age: 5182Age denotes a non-negative integer that represents the time in seconds the object has been in a proxy cache.
< x-timer: S1557441707.643683,VS0,VE0The X-Timer header provides the timing information about the journey of a request from end to end.
S1557441707.643683: The first section of the header (starting with S) represents a Unix timestamp of the start of the request on our edges.VS0: The next section, VS or "varnish start," represents the start of the varnish part of the request's journey and will always be 0.VE0: The last section, VE or "varnish end," represents the sum of the length of the trip. For cache HITs, the length of the trip will nearly always be 0 (not actually zero, but less than a millisecond is rounded down).If there is something wrong with the API request, Contentstack returns an error.
Contentstack uses conventional, standard HTTP status codes for errors, and returns a JSON body containing details about the error. In general, codes in the 2xx range signify success. The codes in the 4xx range indicate error, mainly due to information provided (for example, a required parameter or field was omitted). Lastly, codes in the 5xx range mean that there is something wrong with Contentstack’s servers; it is very rare though.
Let’s look at the error codes and their meanings.
| HTTP status code | Description |
400 Bad Request |
The request was incorrect or corrupted. |
401 Access Denied |
The login credentials are invalid. |
403 Forbidden Error |
The page or resource that is being accessed is forbidden. |
404 Not Found |
The requested page or resource could not be found. |
412 Pre Condition Failed |
The entered API key is invalid. |
422* Unprocessable Entity (also includes Validation Error and Unknown Field) |
The request is syntactically correct but contains semantic errors |
429 Rate Limit Exceeded |
The number of requests exceeds the allowed limit for the given time period. |
500 Internal Server Error |
The server is malfunctioning and is not specific on what the problem is. |
502 Bad Gateway Error |
A server received an invalid response from another server. |
504 Gateway Timeout Error |
A server did not receive a timely response from another server that it was accessing while attempting to load the web page or fill another request by the browser. |
* Contentstack returns the 422 HTTP status code for an error along with the "UID is not valid" message in the response body either when an entry doesn’t exist within the stack, has been deleted from the content type, or exists within a different content type. As the entry has been deleted or unpublished, the Content Delivery Network (CDN) cannot identify the specified entry UID through the cache servers. To check whether the entry has been deleted, try retrieving the entry from CDN first. If the API request fails to retrieve the entry from CDN, then make an API request to the Origin server to check whether the entry exists.
Also, if the content type doesn't exist within the stack, Contentstack returns the 422 HTTP status code for an error along with the "UID is not valid" message in the response body.
Contentstack offers you a Postman Collection that helps you try out our Content Delivery API. You can download this collection, connect to your Contentstack account, and try out the Content Delivery API with ease.
Learn more about how to get started with using the Postman Collection for Contenstack Content Delivery API.
Contentstack provides the OpenAPI files of the Contentstack’s Content Delivery APIs (CDA) that you can use to try out Contentstack APIs on any OpenAPI platform such as Swagger. You can download the OpenAPI JSON file of the Content Delivery API and open it on Swagger Editor to start using it.
Learn more about how to get started with using the OpenAPI files for Contenstack Content Delivery API.
Content type defines the structure or schema of a page or a section of your web or mobile property. To create content for your application, you are required to first create a content type, and then create entries using the content type.
Additional Resource: To get an idea of building your content type as per webpage’s layout, we recommend you to check out our Content Modeling guide.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack.
Note: Branches is a plan-based feature that is available only in the new Contentstack interface.
Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Try
The Get all content types call returns comprehensive information of all the content types available in a particular stack in your account.
When executing the API call, you can add queries to extend the functionality of this API call.
Tip: If any of your content types contains a Global field and you wish to fetch the content schema of the Global field, then you need to pass theinclude_global_field_schema:true parameter. This parameter helps return the Global field's schema along with the content type schema.
To query your content types, under the 'URI Parameters' section, insert a parameter named query and provide the query in JSON format as the value. To learn more about the queries, refer to the Queries section of the Content Delivery API doc.
Note: This API request will return a maximum of 100 content types. To retrieve the next batch of content types, make use of the skip parameter (or refer Pagination for more details).
Try
This call returns information of a specific content type. It returns the content type schema, but does not include its entries.
A Global field is a reusable field (or group of fields) that you can define once and reuse in any content type within your stack. This eliminates the need (and thereby time and efforts) to create the same set of fields repeatedly in multiple content types.
Additional Resource: You can create a dynamic and flexible Global field either by nesting Global field within the Modular Block or Group field within Global field.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack.
Note: Branches is a plan-based feature that is available only in the new Contentstack interface.
Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Try
This call returns comprehensive information of all the global fields available in a particular stack in your account.
Try
This request allows you to fetch comprehensive details of a specific global field.
When executing the API call, in the 'URI Parameters' section, provide the unique ID of your global field.
An entry is the actual piece of content created using one of the defined content types.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack.
Note: Branches is a plan-based feature that is available only in the new Contentstack interface.
Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Try
The Get all entries request fetches the list of all the entries of a particular content type. It returns the content of each entry in JSON format. You need to specify the environment and locale of which you want to get the entries.
Additionally, if you wish to fetch the metadata attached to each entry, then you need to pass include_metadata as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the entry metadata along with all entries in the response body.
You will find the entry metadata under the _metadata key in the response. It will be associated with a specific extension UID as follows:
"_metadata": {
"extensions": {
"{extension_uid}": [{
"image_copyrights": "Contentstack Branding",
"scope": "local"
}]
}
}
If an entry is not published in a specific locale, make use of the “include_fallback=true” query parameter to fetch the published content from its fallback locale.
Note: If the fallback language of the specified locale is the master language itself, this parameter won't be applicable.
To include the publish details in the response, make use of the include_publish_details=true parameter. This will return the publishing details of the entry in every environment along with the version number that is published in each of the environments.
You can add other Queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Add a query parameter named query and provide your query (in JSON format) as the value.
When using Delivery Tokens
include_fallback=true query parameter to fetch the published content from its fallback localeTip: This request returns only the first 100 entries of the specified content type. Refer to the Pagination section to retrieve the rest of your entries in a paginated form.
Try
The Get a single entry request fetches a particular entry of a content type.
Tip: If no version is mentioned, the request will retrieve the latest published version of the entry. To retrieve a specific version, use the version parameter, keep the environment parameter blank, and use the management token instead of the delivery token.
Additionally, if you wish to fetch the metadata attached to each entry, then you need to pass include_metadata as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the entry metadata along with all entries in the response body.
You will find the entry metadata under the _metadata key in the response. It will be associated with a specific extension UID as follows:
"_metadata": {
"extensions": {
"{extension_uid}": [{
"image_copyrights": "Contentstack Branding",
"scope": "local"
}]
}
}
If an entry is not published in a specific locale, make use of the “include_fallback=true” query parameter to fetch the published content from its fallback locale.
Note: If the fallback language of the specified locale is the master language itself, this parameter won't be applicable.
To include the publish details in the response, make use of the include_publish_details=true parameter. This will return the publishing details of the entry in every environment along with the version number that is published in each of the environments.
You can add other Queries to extend the functionality of this API call. Add a query parameter named query and provide your query (in JSON format) as the value.
When using Delivery Tokens
include_fallback=true query parameter to fetch the published content from its fallback localeTry
The Get information on embedded RTE objects request returns comprehensive information on all entries and/or assets embedded within the Rich Text Editor field.
If your entry contains a Rich Text Editor field and you wish to fetch the content schema of the items embedded inside the rich text, then you need to pass the include_embedded_items[]=BASE query parameter.
You can view information about the embedded objects under the _embedded_items parameter in the JSON response body.
Note: Contentstack’s Content Delivery SDKs help consume the embedded entries and assets returned in the API response. You can then render the embedded objects on the front end however required.
Assets refer to all the media files (images, videos, PDFs, audio files, and so on) uploaded in your Contentstack repository for future use. These files can be attached and used in multiple entries.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack.
Note: Branches is a plan-based feature that is available only in the new Contentstack interface.
Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides.
Try
The Get all assets request fetches the list of all the assets of a particular stack. It returns the content of each asset in JSON format. You can also specify the environment of which you want to get the assets.
Additionally, if you wish to fetch the metadata attached to each entry, then you need to pass include_metadata as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the entry metadata along with all entries in the response body.
You will find the entry metadata under the _metadata key in the response. It will be associated with a specific extension UID as follows:
"_metadata": {
"extensions": {
"{extension_uid}": [{
"image_copyrights": "Contentstack Branding",
"scope": "local"
}]
}
}
If an asset is not published in a specific locale, make use of the include_fallback=true query parameter to fetch the published version from the fallback locale.
You can apply Queries to filter assets/entries. Add a query parameter named query and provide your query (in JSON format) as the value.
When using Delivery Tokens
include_fallback=true query parameter to fetch the published asset from its fallback localeTry
The Get a single asset request fetches the latest version of a specific asset of a particular stack.
Tip: If no version is mentioned, the request will retrieve the latest published version of the asset. To retrieve a specific version, use the version parameter, keep the environment parameter blank, and use the management token instead of the delivery token.
Additionally, if you wish to fetch the metadata attached to each entry, then you need to pass include_metadata as a query parameter. Set this parameter to true to include the entry metadata along with all entries in the response body.
You will find the entry metadata under the _metadata key in the response. It will be associated with a specific extension UID as follows:
"_metadata": {
"extensions": {
"{extension_uid}": [{
"image_copyrights": "Contentstack Branding",
"scope": "local"
}]
}
}
If an asset is not published in a specific locale, make use of the include_fallback=true query parameter to fetch the published version from the fallback locale.
When using Delivery Tokens
include_fallback=true query parameter to fetch the published asset from its fallback localeThe Sync API takes care of syncing your Contentstack data with your app and ensures that the data is always up-to-date by providing delta updates.
Note: When executing the following synchronization API Requests, you need to pass the Delivery Token as the value to the access_token parameter.
Try
The Initial Sync request syncs the entries and assets of a stack, published on a specific environment.
Set init to ‘true’ if you want to sync all the published entries and assets. This is usually used when the app does not have any content and you want to get all the content for the first time.
Note: When executing the API request, pass the Delivery Token as the value to the access_token parameter.
Applicable parameters:
| Parameter | Values |
content_type_uid |
Enter content type UID. e.g., productsThis retrieves published entries of specified content type. |
locale |
Enter locale code. e.g., en-usThis retrieves published entries of specific locale. |
start_from |
Enter the start date. e.g., 2018-08-14T00:00:00.000ZThis retrieves published entries starting from a specific date. |
type |
Applicable values are:
If you do not specify any value, it will bring all published entries and published assets. You can pass multiple types as comma-separated values, for example, |
Note: If you specify any value for content_type_uid, locale, start_from, or type, the values for these parameters will remain unchanged for all subsequent sync requests.
Once you perform an initial sync, you will either get a sync_token or a pagination_token in response. These tokens don't have an expiry time.
You can use the sync_token later to perform subsequent sync, which fetches only new changes through delta updates.
If there are more than 100 records, you get a pagination_token in response. This token can be used to fetch the next batch of data. Read Sync using pagination token for more details.
Try
When running the Initial Synchronization or the Subsequent Sync request, if the result of the sync (initial or subsequent) request exceeds 100 records you will get a pagination_token.
The Sync using pagination token request uses the pagination_token to retrieve the next batch of data (100 records) while performing the sync. You can reiterate the process until you get a sync_token.
Note: When executing the API request, pass the Delivery Token as the value to the access_token parameter.
Try
The Subsequent Sync request is used to retrieve the updated content (i.e., published or unpublished content, or any published content that has been deleted) since the last performed complete Sync.
In this API request, you need to provide the sync_token that you received in the last complete sync process. If there are more than 100 records, you will get a pagination_token instead. This token can be used to fetch the next batch of data. Refer the Sync using pagination token section for more details.
Tip: Once you have performed the Initial Sync process, you do not need to perform it again. For retrieving the subsequent delta changes, use the sync_token received either in the Initial Sync process or the previous Subsequent Sync requests to sync new changes. Also, when executing the API request, pass the Delivery Token as the value to the access_token parameter.
Contentstack provides certain queries that you can use to fetch filtered results. You can use queries for Entries and Assets API requests.
You can now pass the branch header in the API request to fetch or manage modules located within specific branches of the stack.
Note: Branches is a plan-based feature that is available only in the new Contentstack interface.
Additionally, you can also set the include_branch query parameter to true to include the _branch top-level key in the response. This key specifies the unique ID of the branch where the concerned Contentstack module resides
Try
Get entries containing the field values matching the condition in the query.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: In the Products content type, you have a field named Title ("uid":"title") field. If, for instance, you want to retrieve all the entries in which the value for the Title field is 'Redmi 3S', you can set the parameters as:
{"title": "Redmi 3S"}
Let’s consider another example. You want to retrieve all the entries that have their start date as 8th December, 2017. Now, you need to set this parameter with the date in the ISO Date format as below:
{ "start_date": "2017-12-08T00:00:00.000Z" }
This will give you all the entries where the start date is 8th December, 2017.
Try
Get entries where the value of a field within a Group field matches the condition in the query. This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Group field.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Card Type ("uid":"card_type"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the value for the Card Type field is 'Debit Card', you can use the following value in the ‘query’ parameter:
{"bank_offers.card_type": "Debit Card"}
Try
Get entries where the value of a field within a Modular Blocks field matches the condition in the query. This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Modular Blocks field.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Blocks field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Deals ("uid":"deals") block. And, within this Deals block, we have a field named Deal Name ("uid":"deal_name"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the value for the Deal Name field is 'Christmas Deal', you can use the following value in the query parameter:
{"additional_info.deals.deal_name": "Christmas Deal"}
Try
Get all the entries in which the value of a field does not match the value provided in the condition.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: In the Product content type, you have a field named Price in USD. Now, you need to retrieve all entries where the value of this field not equal to '146' for this field. The parameter can be used as:
{ "price_in_usd": { "$ne": 146 } }
This will give you all the entries that have the value for Price in USD not set to '146'.
Let’s consider another example. You want to retrieve all the entries except the ones that have their start date as 8th December, 2017. Now, you need to set this parameter with the date in the ISO Date format as below:
{ "start_date": { "$ne": "2017-12-08T00:00:00.000Z" } }
This will give you all the entries where the start date is not 8th December, 2017.
Try
Get entries where the value of a field does not match the value provided in the condition. This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Group field.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Card Type ("uid":"card_type"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the value for the Card Type field is NOT 'Debit Card', use the following value in the query parameter:
{"bank_offers.card_type": {"$ne": "Debit Card"}}
Try
Get entries where the value of a field within the Modular Blocks field matches the condition in the query. This query is specifically for fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Deals ("uid":"deals") block. And, within this Deals block, we have a field named Deal Name ("uid":"deal_name"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the value for the Deal Name field is NOT 'Christmas Deal', use the following value in the query parameter:
{"additional_info.deals.deal_name": {"$ne": "Christmas Deal"}}
Try
Get entries is which the value of a field matches to any of the given values. This parameter will compare field values of entries to that of the values provided in the condition.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Product content type, you have a field named Price in USD. Now, you need to retrieve all the entries where value of this field is one among the given set of values. The query fired using the '$in' parameter is given below:
{ "price_in_usd": { "$in": [ 101, 749 ] } }
This will retrieve all the entries that have the value of Price in USD field set to '101' or 749'.
Try
Get entries where the value of a field, within a Group field, matches any of the given values. This parameter will compare field values of entries to that of the values provided in the condition. This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Group field.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Card Type ("uid":"card_type"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Card Type field are ‘Credit Card’ and 'Debit Card', use the following value in the query parameter:
{"bank_offers.card_type": {"$in": ["Credit Card", "Debit Card"]}}
Try
Get entries where the value of a field within Modular Blocks matches to any of the given values. This query is specifically for fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Deals ("uid":"deals") block. And, within this Deals block, we have a field named Deal Name ("uid":"deal_name"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Deal Name field are 'Christmas Deal’ and ‘Summer Deal', use the following value in the query parameter:
{"additional_info.deals.deal_name": {"$in": ["Christmas Deal", "Summer Deal"]}}
Try
Get all entries in which the value of a field does not match to any of the given values. This parameter will compare field values of entries to that of the values provided in the condition, and the query will retrieve entries that have field values that does not match to any of the values provided.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Product content type, you have a field named Price in USD. Now, you need to retrieve the entries where the field value does not fall in the given set. You can send the parameter as:
{ "price_in_usd": { "$nin": [ 101, 749 ] } }
This will give you all the entries that do not have the value for Price in USD set to '101' or '749'.
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field does not match any of the values provided in the condition. This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Group field.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Card Type ("uid":"card_type"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Card Type field are NOT ‘Credit Card’ and 'Debit Card', use the following value in the query parameter:
{"bank_offers.card_type": {"$nin": ["Debit Card", "Credit Card"]}}
Try
Get entries where the values of the fields within Modular Blocks match the condition in the query. This query is specifically for fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Deals ("uid":"deals") block. And, within this Deals block, we have a field named Deal Name ("uid":"deal_name"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Deal Name field are NOT 'Christmas Deal’ and ‘Summer Deal', use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "additional_info.deals.deal_name": { "$nin": [ "Christmas Deal", "Summer Deal" ] } }
Try
When fetching an entry, the content of referred entries that are part of the parent entry is NOT included in the Response body; you only get their UIDs. To include the content of the referred entries in your response, you need to use the include[] parameter and specify the UID of the reference field as value.
The API request should be as follows:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?include[]={reference_field_UID}
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Product content type, there is a reference field called Categories, which refers entries of another content type. Let’s assume that you had created an entry for the Product content type, and the value selected in the Categories field was ‘Mobiles’. If you fetch the entry using the ‘Get a Single Entry’ API request, you would get all the details of the entry in the response, but the value against the Categories field would be UID of the referenced entry (i.e., UID of the ‘Mobiles’ entry in this case).
In order to fetch the details of the entry used in the Categories reference field, you need to use the include[] parameter in the following manner:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?include[]=categories
In case you wish to fetch the data of the entries of multiple reference fields, use the include[] parameter in the following manner:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?include[]=categories&include[]=brands
Note: The maximum reference depth limit to which a multiple content type referencing Reference field works is three levels deep.
Try
If the reference field is part of a Group field, you need to use the Group field UID as well as the reference field UID using a dot operator.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a Reference field named Bank ("uid":"bank"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve entries and include the data of the reference field as well, you need to use the include[] parameter in the following manner:
https://cda.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?include[]=bank_offers.bank
In case the referenced entry further has reference to another entry (nested referencing), you can use the dot operator to fetch the content of the nested references as well.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: Consider that you have a content type named ‘Blogs’ which has two reference fields (‘Authors’ and ‘Related Articles’) referring to the ‘Author’ and ‘Blogs’ content types (self-referencing), respectively. So, we have the following reference relationships between the content types:
Now, consider that you want to retrieve an entry of the ‘Blogs’ content type along with the data of the author (details from the ‘Author’ content type) who authored the entry. You also want to fetch the data of the authors who wrote the ‘Related Articles’ as well that are referenced in this entry, (details from the ‘Blogs’ content type).
In this case, you need to use related_articles.authors in the include[] parameter as follows:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/content_type_uid/entries?include[]=authors&include[]=related_articles.author
Try
If the reference field is part of a Modular Blocks field, you need to use the Modular Blocks UID, Block UID, as well as the reference field UID using a dot operator.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products’ content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Related Products ("uid":"related_products") block. And, within this Block field, we have a field named Products ("uid":"products"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve entries and include the data of the reference field, you need to use the include[] parameter in the following manner:
https://cda.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?include[]=additional_info.related_products.products
Try
Get entries having values based on referenced fields. This query retrieves all entries that satisfy the query conditions made on referenced fields.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Product content type, if you wish to retrieve all entries that have their brand (Reference field) title set to Apple Inc. So, the query that needs to be run is given below:
{"brand": { "$in_query": { "title": "Apple Inc."}}}
If you have enabled multiple content type referencing, you need to mention the content type UID of the parent content type as follows:
"{"brand":{"$in_query":{"title":"Apple Inc.", "_content_type_uid":"brand"}, "_content_type_uid":"product"}}
You can use queries within this query (nested querying) in order to query on the referred entries. In this case, the syntax of the query will be as follows:
{"reference_field_uid":{"$in_query":{"referred_content_type's_field_uid":{"query_to_be_applied"}}}}{"reference_field_uid":{"$in_query":{"referred_content_type's_field_uid":{"query_to_be_applied"}}}, "_content_type_uid":"UID_of_referred_content_type"}Additionally, to retrieve entries that also include references to entries of multiple content types, you need to specify the content type UIDs of all the referred entries when querying.
For example, “Parent Reference” has a Reference field that points to “Reference content type 1” and “Reference content type 1” has a Reference field that points to both “Reference content type 2” and “Reference content type 3”.
So, to retrieve an entry in “Parent Reference” that has referred to an entry of “Reference content type 1” whose Reference field has referred an entry titled “Sample” of “Reference content type 2”. The query format is as follows:
{"referred_parent_content_type_field_uid": {"$in_query": {"referred_content_type_2_field_uid": { "$in_query": {"title": "Sample"}}}}}{"referred_parent_content_type_field_uid": {"$in_query": {"referred_content_type_2_field_uid": { "$in_query": {"title": "Sample", "_content_type_uid": "referred_content_type_3_uid"} }, "_content_type_uid": "referred_content_type_2_uid"}, "_content_type_uid": "referred_parent_content_type_uid"}}You can use queries within this query (nested querying) in order to to query on the referred entries.
This query will work for entries only.
The syntax of the query will be as follows:
{"reference_field_uid": { "$in_query": { "referred_fieldname": {"query_to_be_applied"}}}}{"reference_field_uid": { "$in_query": { "referred_fieldname": {"query_to_be_applied"}}, "_content_type_uid ":"UID_of_parent_content_type"}}Example: So, extending our previous example, if you want to retrieve all entries that have their brand title that starts with ‘A’, you need to run the query given below:
{"brand": {"$in_query": {"title": {"$regex": "^/a", "$options": "i"}}}}{"brand": {"$in_query": {"title": {"$regex": "^/a", "$options": "i"}, "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_referred_content_type"}, "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_parent_content_type"}}In the above query, ‘Search by Regex’ query has been applied on the referred field. Other queries that can be applied are: Equals Operator, Equals Within Group Operator, Not-equals Operator, Array Equals Operator, Array Not-equals Operator, AND Operator, OR Operator, Less Than, Less Than Or Equal To, Greater Than, Greater Than Or Equal To, and Exists.
Try
Get entries having values based on referenced fields. This query retrieves all entries that satisfy query conditions made on referenced fields.
If the reference field is part of a Group field, you need to mention the Group field UID as well as the reference field UID using a dot operator, as given below.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a Reference field named Bank ("uid":"bank"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the value for the Bank field is ‘Citigroup,’ use the following value in the query parameter:
{"bank_offers.bank": {"$in_query": { "title": "Citigroup"}}}{ "bank_offers.bank": { "$in_query": { "title": "Citigroup", "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_referred_content_type" }, "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_parent_content_type" } }Try
Get entries having values based on referenced fields.
This query retrieves all entries that satisfy query conditions made on referenced fields.
If the reference is part of a Modular Blocks field, you need to mention the Modular Blocks UID, Block UID, as well as the reference field UID using a dot operator
Note that this query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Related Products ("uid":"related_products") block. And, within this Related Products block, we have a field named Products ("uid":"products"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Title field is ‘iPhone 7 128GB', use the following value in the ‘query’ parameter:
{"additional_info.related_products.products": {"$in_query": { "title": "iPhone 7 128GB"}}}{"additional_info.related_products.products": {"$in_query": { "title": "iPhone 7 128GB", "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_referred_content_type"}, "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_parent_content_type"}}Try
Get entries having values based on referenced fields. This query works the opposite of $in_query and retrieves all entries that does not satisfy query conditions made on referenced fields.
Note that this query will work for entries only.
Example: Let’s say you wish to retrieve all entries that have brand names other than Apple Inc. So, the query that needs to be made is given below:
{"brand": {"$nin_query": {"title": "Apple Inc."}}}{ "brand": {"$nin_query": {"title": "Apple Inc.", "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_referred_content_type"}, "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_parent_content_type"}}Note: When querying on Reference field, users need to specify the Content Type UID (using the_content_type_uid parameter) of entry to which the Reference field belongs to.
Try
Get entries having values based on referenced fields. This query works the opposite of $in_query and retrieves all entries that does not satisfy query conditions made on referenced fields.
Note that this query will work for entries only.
If the reference is part of a Group field, you need to use the Group field UID as well as the reference field UID using a dot operator.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a Reference field named Bank ("uid":"bank"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the value for the Bank field is NOT ‘Citigroup', use the following query:
{"bank_offers.bank": {"$nin_query": {"title": "Citigroup"}}}{"bank_offers.bank": {"$nin_query": {"title": "Citigroup", "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_referred_content_type"}, "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_parent_content_type"}}Try
Get entries having values based on referenced fields. This query works the opposite of $in_query and retrieves all entries that does not satisfy query conditions made on referenced fields.
Note that this query will work for entries only.
If the reference is part of a Modular Blocks field, you need to use the Modular Blocks UID, Block UID, as well as the reference field UID using a dot operator.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Related Products ("uid":"related_products") block. And, within this Block field, we have a field named Products ("uid":"products"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the value for the Title field is NOT ‘iPhone 7 128GB', use the following query:
{ "additional_info.related_products.products": {"$nin_query": {"title": "iPhone 7 128GB"}}}{ "additional_info.related_products.products": {"$nin_query": {"title": "iPhone 7 128GB", "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_referred_content_type"}, "_content_type_uid": "UID_of_parent_content_type"}}Try
Get entries by using regular expressions to query fields of a content type. These regex queries will help to retrieve all the entries of a content type that have field values matching the condition provided in the query parameter.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: In the Product content type, you have a field named Color ("uid":"color") in your content type, and you want to retrieve all the entries within this content type that have values for this field starting with 'Bl'. You can use the parameter as:
{ "color": { "$regex": "^Bl" } }.
Now, in order to perform a case-insensitive search, you can use the $options key to specify any regular expressions options:
{ "color": { "$regex": "^bl", "$options": "i" } }.
Tip: Some useful values for $options are m for making dot match newlines and x for ignoring whitespace in regex.
Try
Get entries by using regular expressions to query fields of a Group field. These regex queries will help to retrieve all the entries of a content type that have field values matching the condition provided in the query parameter.
Note: This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a Reference field named Bank ("uid":"bank"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the value for the Card Type starts with “Credit Card,” use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "bank_offers.card_type": { "$regex": "^Credit Card" } }
Try
Get entries by using regular expressions to query fields of a Modular Block. These regex queries will help to retrieve all the entries of a content type that have field values matching the condition provided in the query parameter.
This query will work for entries only and works specifically for fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Deals ("uid":"deals") block. And, within this Deals block, we have a field named Deal Name ("uid":"deal_name"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries where Deal Name starts with “Christmas Deal,” use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "additional_info.deals.deal_name": { "$regex": "^Christmas Deal" }}
Try
Get entries that satisfy all the conditions provided in the '$and' query.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: Let’s say you want to retrieve entries in which the Title field is set to 'Redmi Note 3' and the Color field is 'Gold'. The query to be used for such a case would be:
{"$and":[{"title": "Redmi Note 3"},{"color": "Gold"}]}
The response will contain the entries where the values for Title is 'Redmi Note 3' and Color is 'Gold'.
Try
Get entries that satisfy all the conditions provided in the $and query.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have fields named Card Type ("uid":"card_type") and Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in where the value for Card Type is ‘Credit Card’ and ‘Discount in Percentage’ is '12', use the following value in the query parameter:
{"$and":[{"bank_offers.card_type": "Credit Card"},{"bank_offers.discount_in_percentage": 12}]}
Try
Get entries that satisfy all the conditions provided in the $and query.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Deals ("uid":"deals") and Rating ("uid":"rating") blocks. And, within the Deals and Rating blocks, we have the Deal Name ("uid":"deal_name") and Stars ("uid":"stars") fields, respectively. If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in where the values for Deals and Ratings fields are ‘Christmas Deal’ and '2', respectively, use the following value in the query parameter:
{"$and":[{"additional_info.deals.deal_name": "Christmas Deal"},{"additional_info.rating.stars": 2}]}
Try
Get all entries that satisfy at least one of the given conditions provided in the '$or' query.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: Let’s say you want to retrieve entries in which either the value for the Color field is 'Gold' or 'Black'. The query to be used for such a case would be:
{ "$or": [{ "color": "Gold" }, { "color": "Black" }] }
The response will contain the entries that have their Color fields set to either 'Gold' or 'Black'.
Try
Get all entries that satisfy at least one of the given conditions provided in the $or query.
This query is specifically for entries and works for fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have fields named Card Type ("uid":"card_type") and Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries where either the value for Card Type is ‘Debit Card’ or the value for Discount in Percentage is '12', use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "$or": [{ "bank_offers.card_type": "Debit Card" }, { "bank_offers.discount_in_percentage": 12}]}
Try
Get all entries that satisfy at least one of the given conditions provided in the '$or' query.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the ‘Products’ content type, we have a Modular Group field named ‘Additional Info’ ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Deals ("uid":"deals") and Rating ("uid":"rating") blocks. And, within the Deals and Rating blocks, we have the Deal Name ("uid":"deal_name") and Stars ("uid":"stars") fields, respectively. If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries where either the value for Deal Name is ‘Christmas Deal’ or the value for Stars is '2', respectively, use the following value in the query parameter:
{"$or":[{"additional_info.deals.deal_name": "Christmas Deal"},{"additional_info.rating.stars": 2}]}
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is lesser than the value provided in the condition.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: Let’s say you want to retrieve all the entries that have value of the Price in USD field set to a value that is less than but not equal to 600. You can send the parameter as:
{ "price_in_usd": { "$lt": 600 } }
This will give you all the entries of mobile phones costing less than but not equal to $600.
Let’s consider another example. You want to retrieve all the entries that have their start date before 8th December, 2017. Now, you need to set this parameter with the date in the ISO Date format as below:
{ "start_date": { "$lt": "2017-12-08T00:00:00.000Z" } }
This will give you all the entries where the start date is before 8th December, 2017, but you will not get the entries of the same date.
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is lesser than the value provided in the condition.
This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Discount in Percentage field is less than ‘25’, use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "bank_offers.discount_in_percentage": { "$lt": 25 } }
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is lesser than the value provided in the condition.
This query is specifically for fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Rating ("uid":"rating") block. And, within this Block field, we have a field named Stars ("uid":"stars"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Stars field is less than ‘3’, use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "additional_info.rating.stars": { "$lt": 3 } }
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is lesser than or equal to the value provided in the condition.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: Let’s say you want to retrieve all the entries that have value of the Price in USD field set to a value that is less than or equal to 146. To achieve this, send the parameter as:
{ "price_in_usd": { "$lte": 146 } }
This will give you all the entries of mobile phones costing less than and equal to $146.
Let’s consider another example. If you want to retrieve all the entries that have their start date before and on 8th December, 2017. Now, you need to set this parameter with the date in the ISO Date format as below:
{ "start_date": { "$lte": "2017-11-08T00:00:00.000Z" } }
This will give you all the entries before 8th December, 2017, along with the entries of 8th December, 2017.
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is lesser than or equal to the value provided in the condition.
This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Discount in Percentage field is less than or equal to ‘25’, use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "bank_offers.discount_in_percentage": { "$lte": 25 } }
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is lesser than or equal to the value provided in the condition.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Rating ("uid":"rating") block. And, within this Rating block, we have a field named Stars ("uid":"stars"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Stars field is less than or equal to ‘3’, use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "additional_info.rating.stars": { "$lte": 3 } }
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value for a field is greater than the value provided in the condition.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: Let’s say you want to retrieve all the entries that have value of the Price in USD field set to a value that is greater than but not equal to 146. You can send the parameter as:
{ "price_in_usd": { "$gt": 146 } }
This will give you all the entries of mobile phones costing greater than and not equal to $146.
Let’s consider another example. If you want to retrieve all the entries that have their start date later than 8th December, 2017. Now, you need to set this parameter with the date in the ISO Date format as below:
{ "start_date": { "$gt": "2017-11-08T00:00:00.000Z" } }
This will give you all the entries after 8th December, 2017.
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value for a field is greater than the value provided in the condition.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Discount in Percentage field is greater than ‘25’, use the following value in the query parameter:
{ "bank_offers.discount_in_percentage": { "$gt": 25 } }
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value for a field is greater than the value provided in the condition.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Rating ("uid":"rating") block. And, within this Block field, we have a field named Stars ("uid":"stars"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Stars field is greater than ‘3’, use the following value in the query parameter:
{"additional_info.rating.stars": {"$gt": 3}}
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is greater than or equal to the value provided in the condition.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: Let’s say you want to retrieve all the entries that have value of the Price in USD field set to a value that is less than and equal to 146. You can send the parameter as:
{ "price_in_usd": { "$gte": 146 } }
This will give you all the entries of mobile phones costing greater than and equal to $146.
Let’s consider another example. You want to retrieve all the entries that have their start date 8th December, 2017, and later. Now, you need to set this parameter with the date in the ISO Date format as below:
{ "start_date": { "$gte": "2017-11-08T00:00:00.000Z" } }
This will give you all the entries where the start date falls after 8th December, 2017, along with the entries of the same date.
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is greater than or equal to the value provided in the condition.
This query is specifically for fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Discount in Percentage field is greater than or equal to ‘25’, use the following value in the query parameter:
{"bank_offers.discount_in_percentage": { "$gte": 25 } }
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
Get entries in which the value of a field is greater than or equal to the value provided in the condition.
This query is specifically for fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Rating ("uid":"rating") block. And, within this Rating block, we have a field named Stars' ("uid":"stars"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Stars field is greater than or equal to ‘3’, use the following value in the query parameter:
{"additional_info.rating.stars": {"$gte": 3}
Note: Avoid using seconds and milliseconds in date/time queries. We recommend to round off to the nearest minute (at most 5 minutes).
Try
The limit parameter will return a specific number of entries in the output. So for example, if the content type contains more than 100 entries and you wish to fetch only the first 2 entries, you need to specify '2' as value in this parameter.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&limit=2
Try
The skip parameter will skip a specific number of entries in the output. So, for example, if the content type contains around 12 entries and you want to skip the first 2 entries to get only the last 10 in the response body, you need to specify ‘2’ here.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&skip=2
Try
When fetching entries, you can sort them in the ascending order with respect to the value of a specific field in the response body.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: In the Product content type, if you wish to sort the entries with respect to their prices, the parameter can be used as:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&asc=price_in_usd
This will give you all the entries sorted in the ascending order with respect to the Price in USD field.
Try
Sort your fetched entries in the ascending order with respect to the value of a specific field in the response body.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve entries in the ascending order with respect to the Discount in Percentage field, use the following URL:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&asc=bank_offers.discount_in_percentage
Try
When fetching entries, you can sort your fetched entries in the ascending order with respect to the values of any block within a Modular Block field.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Note: Currently, this query is not applicable for Reference fields within Modular Blocks.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Block field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Rating ("uid":"rating") block. And, within this Rating block, we have a field named Stars ("uid":"stars"). Use the following URL to retrieve entries in ascending order based on the values of the Stars field:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&asc=additional_info.rating.stars
Try
When fetching entries, you can sort them in the descending order with respect to the value of a specific field in the response body.
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: In the Product content type, if you wish to sort the entries with respect to their prices, the parameter can be used as:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&desc=price_in_usd
This will give you all the entries sorted in the descending order with respect to the Price in USD field.
Try
Sort your fetched entries in the descending order with respect to the value of a specific field in the response body.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve entries in the descending order with respect to the values of the Discount in Percentage field, use the following URL:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&desc=bank_offers.discount_in_percentage
Try
Sort your fetched entries in the descending order with respect to the value of a specific field in the response body.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Note: Currently, this query is not applicable for Reference fields within Modular Blocks.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Rating ("uid":"rating") block. And, within this Rating block, we have a field named Stars ("uid":"stars"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve entries in the descending order with respect to the values of the Stars field, use the following URL:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&desc=additional_info.rating.stars
Try
Get entries if value of the field, mentioned in the condition, exists.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Product content type, we have a field named Price in USD. Now, you want to retrieve all the entries in the content type in which the field exists. You can send the parameter as:
{ "price_in_usd": { "$exists": true } }.
Try
Get entries if value of the field, mentioned in the condition, exists.
This query is specifically for entries and work on fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Card Type ("uid":"card_type"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Discount in Percentage field exists, use the following value in the query parameter:
{"bank_offers.discount_in_percentage": { "$exists": true }}
Try
Get entries if value of the field, mentioned in the condition, exists.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Deals ("uid":"deals") block. And, within this Block field, we have a field named Deal Name ("uid":"deal_name"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the entries in which the values for the Stars field exists, use the following value in the query parameter:
{"additional_info.rating.stars": {"$exists": true }}
Try
The only[][] parameter will include the data of only the specified fields for each entry and exclude the data of all other fields. There are two approaches to this parameter. Firstly, we have the only[BASE][] parameter, where 'BASE' is the default value and refers to the top-level fields of the schema. Secondly, we have the only[Reference_field_uid][] parameter, where you need to enter the UID of the reference field in place of "Reference_field_uid".
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Product content type, if we need to retrieve the data of only the Price in USD parameter of all the entries, you can send the parameter as:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/author/entries?environment=production&only[BASE][]=price_in_usd
Try
Get entries in which the data of a specific field is included in the response JSON.
This query is specifically for entries and works on fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products’ content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve only the values of the Discount in Percentage field of all the entries, you can send the parameters as:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&only[BASE][]=bank_offers.discount_in_percentage
Try
Get entries in which the data of a specific field is included in the response JSON.
This query is specifically for fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Rating ("uid":"rating") block. And, within this Rating block, we have a field named Stars ("uid":"stars"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve the values of all the Stars field from all the entries, you can send the parameters as:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&only[BASE][]=additional_info.rating.stars
Try
The except[][] parameter will exclude the data of the specified fields for each entry and will include the data of the rest of the fields. There are two approaches to this parameter. Firstly, we have the except[BASE][] parameter, where 'BASE' is the default value and refers to the top-level fields of the schema. Secondly, we have the except[Reference_field_uid][] parameter, where you need to enter the UID of the reference field in place of Reference_field_uid.
This query will work for entries only.
Example: In the Product content type, if we need to retrieve the data of entries of all the other fields except the Price in USD parameter, you can send the parameter as:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&except[BASE][]=price_in_usd
Try
Get entries in which the data of a specific field is excluded from the response JSON, but the data of the rest of the fields are included.
This query is specifically for entries and works with fields that are part of the Group field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Group field named Bank Offers ("uid":"bank_offers"). And, within this Group field, we have a subfield named Discount in Percentage ("uid":"discount_in_percentage"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve all the entries of a content type, but exclude the data for the Discount in Percentage field in the JSON response, you can send the parameters as:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&except[BASE][]=bank_offers.discount_in_percentage
Try
Get entries in which the data of a specific field is excluded from the response JSON, but the data of the rest of the fields are included.
This query is specifically for entries and works with fields that are part of any block within a Modular Block field.
Example: In the Products content type, we have a Modular Group field named Additional Info ("uid":"additional_info") that contains the Rating ("uid":"rating") block. And, within this Block field, we have a field named Stars ("uid":"stars"). If, for instance, you want to retrieve all the entries of a content type, but exclude the data for the Stars field in the JSON response, you can send the parameters as:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment=production&except[BASE][]=additional_info.rating.stars
Try
To retrieve the count of entries, we have two parameters: include_count (retrieves entries' details and their count) and count (retrieves only the count of entries).
This query will work for both entries as well as assets.
Example: If you wish to know the total number of entries in the Product content type and also retrieve all the data, you need to run the following API request:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment={environment}&include_count=true
To get only the count, run the following API request:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment={environment}&count=trueTry
The 'Get all entries' API request returns only the first 100 entries of the specified content type. Similarly, the 'Get all assets' request fetches the first 100 assets of a particular stack.
In both requests, first, use the include_count parameter to get the total count of the items (entries/assets). Learn more about the Count parameter.
Since only 100 items are returned at a time in your response (in case of both requests), you can get the rest of the items in batches using the skip parameter in subsequent requests. Learn more about the Skip parameter.
You can paginate the output of a request by using the limit parameter. For example, if your have 200 entries and/or assets and you want to retrieve them all but display only 10 items at a time. Use the limit=10 and skip=10 parameters, to get them all but display only 10 items per page.
The syntax of the pagination request will look like the following:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/product/entries?environment={environment}&locale={locale}&include_count=true&skip={skip_value}&limit={limit_value}https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/assets?environment={environment_name}&include_dimension={boolean_value}&include_count=true&skip={skip_value}&limit={limit_value}The table below contains the list of all query parameters used in the Content Delivery APIs. Each query parameter within the table has a corresponding description, the API requests it is used in, and a relevant example. Use it as a cheat sheet or quick reference to search API requests by query parameters.
The Contentstack Postman collection is a set of preconfigured REST API requests that will make it easy for you to get started with the Contentstack APIs and try out our API requests through the popular Postman REST client.
To use the Contentstack Postman collection you will need to have the Postman. You can either download the Desktop app or use Postman for Web.
Note: If you have already installed Postman for your device, go to the Download Latest Postman Collection for Contentstack section.
Postman is available for Windows (x32), Windows (x64), Mac (Intel Chip / Apple Chip), and Linux environments.
Once you have installed Postman for your device, click on the Run in Postman button.
Note: The Contentstack Postman collection does not support the now deprecated Postman Chrome extension. Make sure you have installed the latest version of the Postman desktop app
Select either Postman for Web or Postman for Windows option from the following modal.
When you select any one of the options, it results in the Import Collection modal. Select your workspace and import the collection that covers all the Content Delivery API endpoints for Contentstack.
After selecting the appropriate variant of Postman, the collection will open the Postman app and appear in the left pane:
Note: To query the European endpoint for Contentstack's Content Delivery API, you need to download the Content Delivery API - Europe Environment file for the Europe region and import it in your Postman environment manually.
We have also hosted our Postman collection on GitHub. You can follow the steps mentioned in the Readme file to download and start using it.
You can also choose to watch the latest Postman collection to get notifications of new releases or updates.
To do so, click on the following Watch button and select Watching.
When you download and install the latest version of the Content Delivery API (CDA) Postman collection, you also download and import the respective environment along with the environment variables.
Once your environment is imported, next you need to set your Contentstack account specific values.
Note: As these environment variables are referenced across multiple API requests, once you set the variables, it becomes a lot more convenient to make repeated use of the Postman collection.
Some of the important variables that you need to set are as follows:
| Environment Variable | Value |
| base_url | cdn.contentstack.io |
| api_key | your_stack_api_key |
| access_token | your_environment-specific_delivery_token |
Note: The Contentstack Postman collection will require a valid environment-specific Delivery token to make API calls. Check out the Authentication section for more details.
If you want to add your own environment variables, you can follow the procedure in the next section.
To add any new environment variables for your Postman collection, perform the following steps:
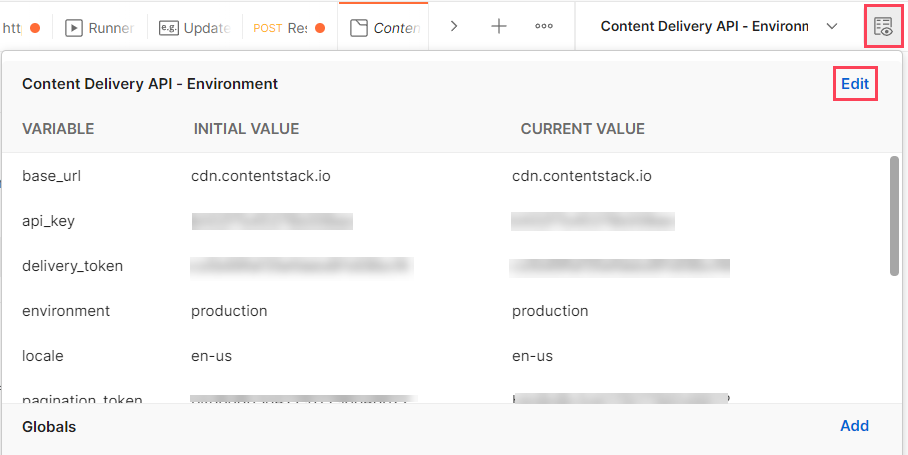
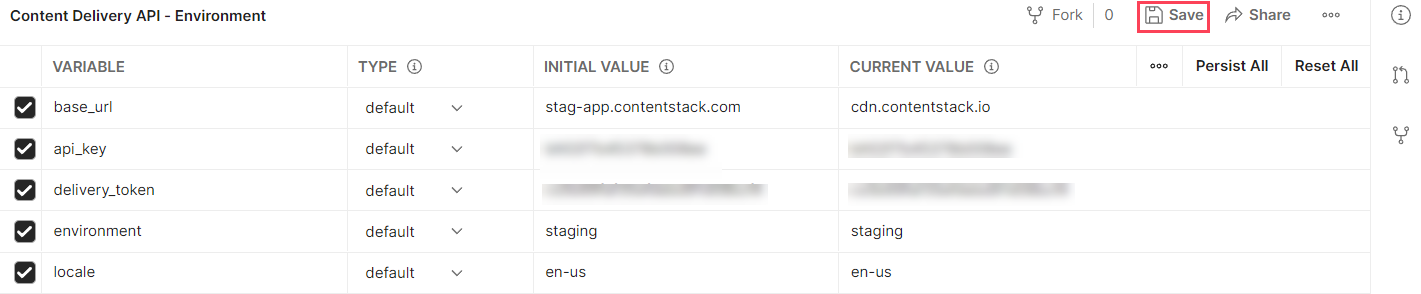
With every new API request added, we update our environment file. So, to get the latest environment variables, you need to download the collection along with the updated environment file again, compare your existing environment with the latest environment, identify and add the new variables to your existing environment.
Next, let’s see how you can run API Requests from your Contentstack Postman collection using your environment.
With the Contentstack Postman Collection loaded into the Postman app (on the left pane) and the environment created, you can now make API requests to the Contentstack API via Postman.
To make an API request, perform the following steps:
Note: If you want to make changes to your parameters or want to add parameters of your own, you can do it here.
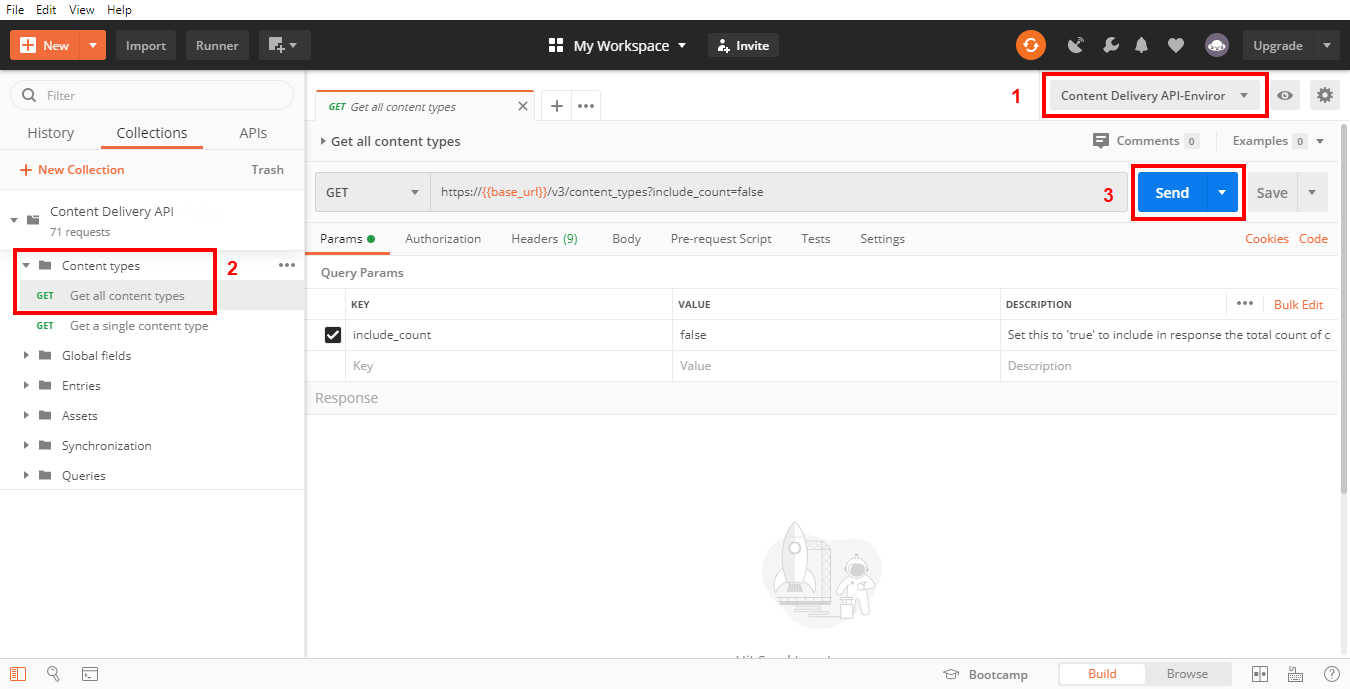
The API call should return with a response under the Body tab in the bottom half of the screen.
Contentstack provides certain queries that you can use to fetch filtered results. You can use queries for Entries and Assets API requests.
You can add queries to extend the functionality of an entry-specific API call. To add a query, you can either append the query parameter directly to the entry URL or append the query parameter along with your conditional query (in JSON format) to the entry URL.
Case 1: Append the query parameter
If you want to return a specific number of entries in your response output, you can use the limit query parameter. For example, if you want to retrieve only the first 2 entries of a content type, pass '2' as the value for the limit parameter.
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/{{content_type_uid}}/entries?limit=2
Case 2: Append the conditional query
If you want to retrieve all the entries of a content type in which the value for the Title ("uid":"title") field is “ABC”, you can append the query parameters to the entry URL as follows:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/{{content_type_uid}}/entries?query={"title": "ABC"}
Let’s say you want to retrieve all the entries that have their start date as 8th December 2017. Now, you need to append the query with the start date in the ISO Date format as below:
https://cdn.contentstack.io/v3/content_types/{{content_type_uid}}/entries?query={ "start_date": "2017-12-08T00:00:00.000Z" }
You can append multiple queries in a single API Request as follows:
{{entry_URL}}?environment={{environment}}&locale={{locale}}&include_count=true&skip={skip_value}&limit={limit_value}
You can use Image Delivery APIs by appending queries to the image URL:
{{image_url}}?query_parameter
For example, to resize the width of an image to 100px, you need to append ?width={100} to the image URL. So, the API request would be:
https://images.contentstack.io/v3/assets/blteae40eb499811073/bltc5064f36b5855343/59e0c41ac0eddd140d5a8e3e/image_name?width=100.
You can also use multiple queries in a single API request as follows:
{{image_url}}?width={width_value}&height={height_value}&resize-filter={resize-filter_value}We strongly advise against storing your API keys and tokens in your collection permanently. If you or someone else shares the collection by mistake, other users will be able to export it along with these keys.
We recommend that you provide your Contentstack account-specific API keys and tokens in your environment or directly to the sample requests.
We keep our Postman Collection updated. To get the latest version of our Postman Collection, all you need to do is to download the Postman Collection along with the updated environment again and you are good to go.
You can also choose to watch for the latest Postman Collection updates on our GitHub repository and get notifications of new releases or updates to the repository. The GitHub Readme doc will help you with the steps that you need to follow.
When trying out Contentstack Get Entry or Get All Entries API requests, Contentstack recommends certain optimization measures that will help you achieve fair limits on your API usage.
Here are some important points that you need to consider:
So what do you do if you might hit the limits even after following the above precautionary measures?
In this scenario, you can make use of filtering or pagination. What does this mean? Let’s look at the steps involved:
In order to attain and maintain optimum performance and ensure that infrastructure resources are used in an efficient manner, Contentstack recommends certain best practices.
By following the recommendations discussed in this guide, you can maintain reasonable API usage while making calls or querying for data by minimizing the number of includes in your call.
Optimize your code to eliminate any redundancies or duplicates from the includes, unwanted includes, or references from our code.
We may get faster responses, however, it can result in retrieving stuff in the response that we don't really need. Before making a call, check for queries in the code that will fetch data items that aren’t used in your application, check whether the fetched data is being put back with no changes made to them, and so on. Also, you can avoid making queries unique by putting in a random number or timestamp.
Once you have optimized your code, cache data items that you use more frequently. Your cache management system can be programmed to help you retrieve most frequently used data through the cache instead of the server.
For example, in a user management application where you update various user details such as user groups, titles, and so on. In such a case, you can think of keeping these details on the application side rather than retrieving them through calls every time the user opens the form.
If you posses content pieces that do not change often, they can be cached in your app's cache management system to avoid fetching them every now and then.
For example, if your app is customer facing and there is an FAQ section in your app, you can prefer keeping answers to these FAQs on the application cache rather than fetching it every time where there is a requirement.
Contentstack webhooks can be used to keep track of changes. You can set webhooks when any changes are made to content or code and then react as required.
The webhook notifications allow App to fetch details as desired instead of waiting for the app's API instance to check for job status periodically and then fetch the data. Webhooks can help you in such situations by notifying you as and when the job gets completed.
This reduces the number of includes in the call that may otherwise be high if the checking period has considerable time in between.
Lazy loading, or "On-demand loading," is an online content optimization technique for web apps and websites. It involves loading the most important section of the page first followed by the remaining sections, instead of loading and rendering the complete page in one go. This totally depends on the user requirement.
This approach can be useful in reducing the number of includes involved in making a call and rendering the content to the user. This is not only cost-effective but also resource effective as well.
Referencing is a powerful Contentstack feature that allows you to create references. However, if not needed, we encourage you to avoid fetching unnecessary references in the response.
The number of includes in case of referencing is one thing, but the depth of a single include is also more resource costly than a shallower include. So you should always decide logically when retrieving data in a single call and avoid retrieving them unnecessarily for optimum resource utilization.
When making use of multiple content type references, and fetching the schema of all these content types can be exhausting. This also increases the number of includes in a call.
This case can be handled efficiently by using Modular Blocks. They can be used with other modules to construct a complete webpage. You can create multiple blocks (let's say, B1, B2, B3, and so on with each block with a different schema) within a modular block while creating a content type.
While creating an entry in this content type, you can add data to any of the blocks (B1, B2, B3) and keep other blocks empty. And now when you make a call, you don't have to include the referenced content types in your call. This is another way of minimizing the includes in your call or queries.
Was this article helpful?
Thanks for your feedback